Note: This repository is currently being updated.
This repository provides a benchmark for question answering on Human-Centric Tables (HCTs). HCTs are non-relational tables with complex structures, making them difficult to parse and understand. This benchmark enables the evaluation of large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) on both real-world and synthetic HCTs.
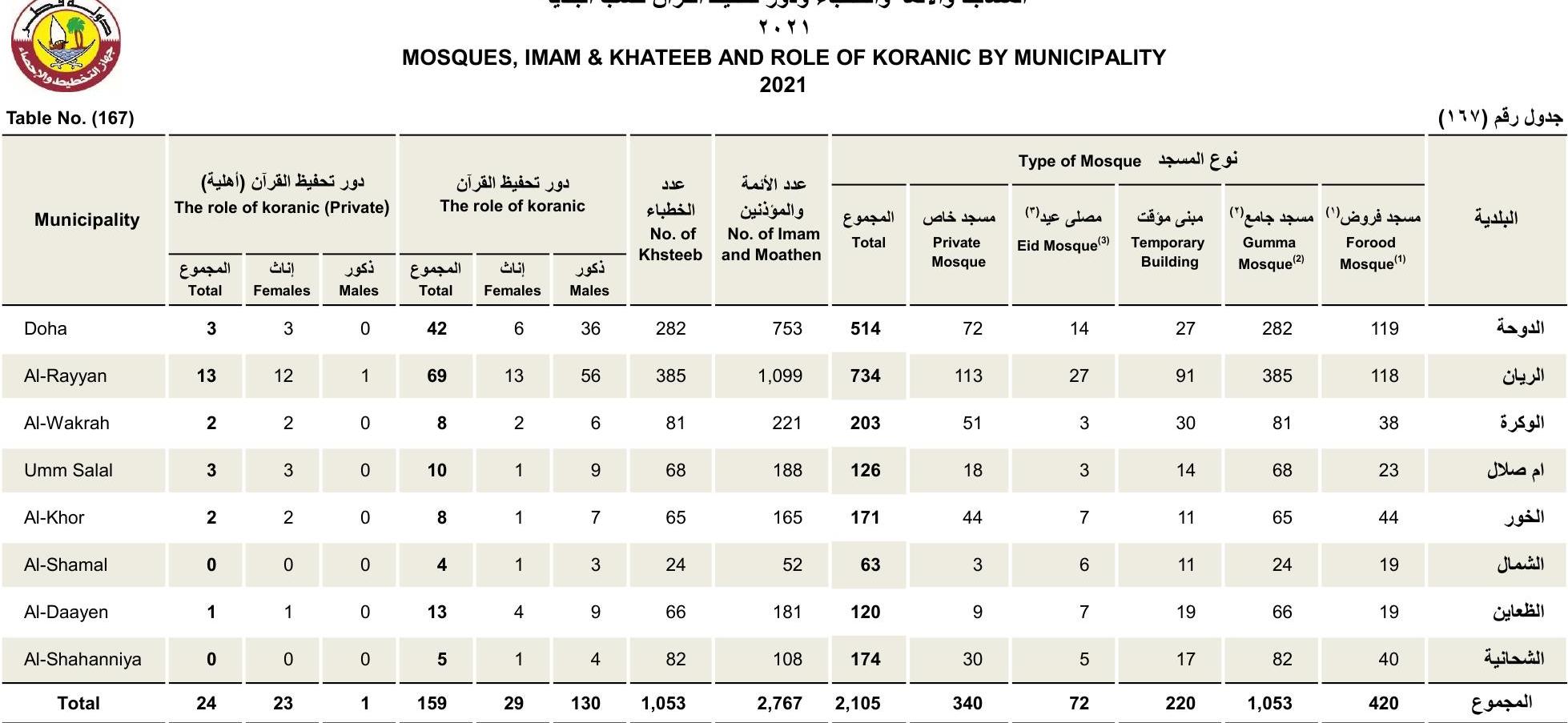
Example of HCT:
Details of the benchmark methodology and dataset can be found in our upcoming paper (link to be added).
├── datasets/ # All benchmark data
│ ├── realWorld_datasets/ # Real-world HCT dataset
│ │ ├── prompts/
│ │ ├── qaps/ # Question–answer pairs (real-world)
│ │ └── tables/ # Compressed HCT tables (images, CSVs, HTMLs, MDs)
│ └── synthetic_datasets/ # Synthetic HCT datasets
│ ├── original/ # Original synthetic tables (CSV, HTML, MD)
│ └── text_obfuscated/ # Synthetic tables with obfuscated text content (CSV, HTML, MD)
│
├── synthetic_data_generator/ # Synthetic HCT data generation system
│ ├── generator_code/ # R scripts for table and QA synthesis
│ ├── prompts/ # Synthetic prompts used for text-based generation
│ ├── synthetic_data_per_semantic_template/ # Example generated synthetic tables (zipped)
│ ├── HCTexample.png # Example table visualization
│ └── README_SYNTHETIC_GENERATOR.md # Detailed guide for running the generator
│
├── scripts/ # Code used for experiments and model evaluation
│ ├── inference_experiments/ # Inference pipelines for LLMs and VLMs
│ │ ├── llm_inference/ # Runs table QA with text-only models
│ │ └── vlm_inference/ # Runs table QA with vision–language models
│ ├── score_model_responses/ # Scoring and evaluation utilities
│ │ ├── helper_for_vision_scoring.json # Helper config for VLM scoring
│ │ └── score_responses.py # Scores model responses (LLM + VLM)
│ └── finetuning/ # Configuration for fine-tuning experiments
│ ├── config_yamls/ # YAMLs for LLAMA-Factory fine-tuning runs
│ └── datatset_prep_for_llama_factory/ # Converts HCT-QA data into Alpaca-style JSON
│
├── results/ # Example model outputs and evaluation scores
│ ├── model_responses/ # Sample LLM/VLM response files
│ ├── model_responses_for_experiments_in_paper/ # Model responses files used in paper's experiments
│ └── scores/ # Example evaluation score files
│
├── format_files.sh # Script to uncompress and organize all datasets
├── requirements.txt # Dependencies for running benchmarks and scripts
└── README.md # Main documentation file
This is the first thing you should run as this will uncompress all the necessary folders and files and prepare it for the scripts
chmod +x ./format_files.sh
./format_files.sh
qaps/: Contains question-answer pairs.tables/: HCTs provided as compressed.gzfiles (CSV and images).
The data is also available in HuggingFace
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("qcri-ai/HCTQA")Ground Truth Format:
The gt attribute in the prompts and qaps files present the answer in the following format:
- Values from the same row are encased in
{}and within that values from different columns are separated by| - Values from different rows are separated by
|| - Aggregations are put in
{}and multiple distinct aggregations are separated by||
This format allows for more detailed evaluation of the models.
This module allows users to generate synthetic HCTs with different styles and properties for experimentation.
Refer to synthetic_data_generator/README_SYNTHETIC_GENERATOR.md for details. Details of the template types used to create the questions for these synthetic tables can also be found in that README file.
We recommend using Python 3.12 and a virtual environment (e.g., Conda):
conda create --name hct_benchmark python=3.12 -y
conda activate hct_benchmark
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Some models require access via Hugging Face. Create a .env file in the "HCT-QA-Benchmark" folder:
echo "HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN=<your_token_here>" > .env
Replace <your_token_here> with your actual Hugging Face API Token.
To run experiments with text-only LLMs run:
cd /scripts/inference_experiments/llm_inference
python llm_inf.py --model_name_or_path "google/gemma-3-12b-it" --output_folder "../../results/model_responses/llms/" --data_source_type "real" --split_name "all" --batch_size 32 --num_gpus 1 --use_system_prompt TrueThe parameters for this command are:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--model_name_or_path |
Path to local or huggingface model. "all" for models used in the paper. |
--output_folder |
Path to folder where model responses will be stored. |
--data_source_type |
"real", "synthetic", "all" to choose what type of HCTs to run inference on. |
--split_name |
"train", "validation", "test" or "all" to choose which split of data to run inference on |
--batch_size |
Batch size for inference |
--num_gpus |
Number of available GPUs to run parallel inference on, default = 1. |
--use_system_prompt |
Boolean to determine whether to use system prompt or not (some models like gemma-2 do not support system prompting) |
To run experiments with vision-text VLMs run:
cd /scripts/inference_experiments/vlm_inference
python vllm_inference.py --model "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct" --num_gpus 2 The parameters for this command are:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--model |
Path to local or huggingface model. "all" for models used in the paper. |
--output_folder |
Path to folder where model responses will be stored. |
--qaps_file |
path to the qaps file (normally in "datasets/realWorld_datasets/qaps") |
--num_gpus |
Number of available GPUs to run parallel inference on, default = 1 |
We provide a script that scores the model responses outputted by the LLM Inference scripts detailed above. To run the scores run:
cd /scripts/score_model_responses
python score_responses.py --folder_name /path/to/folder --output_file /path/to/output.txt --print_results --mode visionThe parameters for this command are:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--folder_name |
Folder where model responses are stored. (this should be the --output_folder argument from the inference_experiments commands). |
--output_folder |
Path to a TXT FILE where model scores will be written to. |
--print_results |
True, to print results to console in addition to writing to output file. Otherwise, False.") |
--mode |
"real" for results on text-only Real HCTs, "synthetic" for results on text-only Synthetic HCTs, "vision" for results on vision-text modality |
We use (LLAMA-Factory)[https://github.com/hiyouga/LLaMA-Factory] to fine-tune our models.
Here are the steps to replicate the training:
- Clone LLAMA-Factory repository
git clone https://github.com/hiyouga/LLaMA-Factory.git- Create custom dataset for finetuning using the script we provide
cd /scripts/finetuning/datatset_prep_for_llama_factory
python3 create_hctqa_in_alpacaJson.py --path_to_datasets_json_file ~/LLaMA-Factory/data/dataset_info.json --path_to_main_llama_factory_folder ~/LLaMA-FactoryFor the --path_to_datasets_json_file argument provide the path to the dataset_info.json file in your lcoal cloned LLAMA-Factory directory. This file should already exist when you clone.
For the --path_to_main_llama_factory_folder argument provide the path to the main LLaMA-Factory folder when you clone the repo (the parent folder that contains all their files anc code).
-
Create a config.yaml file for finetuning. Example files are provided in
/scripts/finetuning/config_yamls/ -
Copy your config.yaml file into the main
/LLaMA-Factoryfolder inside your cloned repo. Do not skip this step as the LLaMA-Factory scripts expect this config to be in the same directory. -
Run the train command (from the inside the /LLaMA-Factory folder):
llamafactory-cli train <path to your config.yaml that should be in the main /LLaMA-Factory folder- Leaderboard: We are working on a comprehensive leaderboard that includes all the models tested in the paper and many more recent ones.
- Expanding the Dataset: We are currently expanding the dataset by including more real world HCTs from a variety of new sources.
Stay tuned for updates!
If you use this benchmark, please cite our work (citation details will be added once the paper is published).
We welcome contributions! Please submit issues or pull requests to improve the benchmark.
This repository is licensed under the MIT License.