Task - Arrays - Multidimensional Arrays #90
Replies: 25 comments
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
/*Write a program that declares a 2 x 3 array with the following values:
5 6 7
8 9 10
Print the array row-by-row, so your output looks like this:
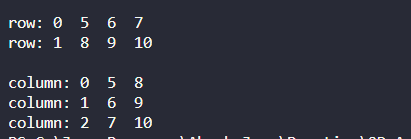
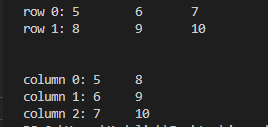
row 0: 5 6 7
row 1: 8 9 10
Then print the array column-by-column, so your output looks like this:
col 0: 5 8
col 1: 6 9
col 2: 7 10 */
class Sample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = {{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(); //Once data entered then new line for new row
System.out.printf("row: %d",i);
for (int j=0; j<a[i].length; j++) { //row wise printing
System.out.print(" "+a[i][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
for (int j=0; j<3; j++) { //Column wise printing
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("column: %d",j);
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
System.out.print(" "+a[i][j]);
}
}
}
}2public class MultiArray2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] ={{1,2},{3,4}};
int b[][] ={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int productArray[][] =new int[2][3];
if(a[0].length == b.length){
System.out.println("Multipilcation is possible");
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println();
for(int j = 0;j<3; j++) {
productArray[i][j]=0;
for(int k = 0; k <2 ; k++) {
productArray[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
System.out.print(productArray[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}3public class MultiArray3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
int rows = a.length;
int cols1 = a[0].length;
int cols2 = a[1].length;
int cols3 = a[2].length;
if (rows == cols1 && rows == cols2 && rows == cols3) {
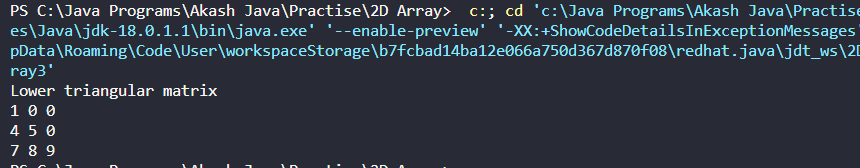
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
if (j > i) {
System.out.print("0 ");
} else {
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("the lower triangular matrix needs to be a square matrix");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1_PrintMultiDimArraypackage Array.MultidimensionalArray;
public class printMultiDimArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int marr[][]=new int[2][3]; //two dimension array declaration
marr[0][0]=5;
marr[0][1]=6;
marr[0][2]=7;
marr[1][0]=8;
marr[1][1]=9;
marr[1][2]=10;
// alternate method-int marr[][]={{5,6,7,},{8,9,10}}
System.out.println("Printing the array row-by-row");
// printing row-wise
for (int i=0; i<marr.length; i++){
System.out.print("row " + i+": ");
for(int j=0; j<marr.length+1; j++){
System.out.print(marr[i][j]+"\t ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Printing the array column-by-column: ");
//printing column wise
for (int i=0; i<marr.length+1; i++){
System.out.print("col " + i+": ");
for(int j=0; j<marr.length; j++){
System.out.print(marr[j][i]+"\t ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output:2_MatrixMultiplicationpackage Array.MultidimensionalArray;
public class MatrixMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrixA = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
int[][] matrixB= { { 7, 8 }, { 9, 10 }, { 11, 12 } };
int[][] matrixC= new int[2][2];
int row1 = matrixA.length;
int column1 = matrixA[0].length;
int row2 = matrixB.length;
int column2 = matrixB[0].length;
if(column1 == row2){
System.out.println("\nMultiplication Possible");
System.out.println("Resultant matrix will have "+ row1 + "X" + column2+ " dimension.");
System.out.print("\nMatrix Multiplication:\n");
for(int i=0;i<row1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<column2;j++){
matrixC[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0; k<column1;k++){
matrixC[i][j]+=matrixA[i][k]*matrixB[k][j];
}
System.out.print(matrixC[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Multiplication Not Possible");
}
}
}Output:3_LowerTriangularMatrixpackage Array.MultidimensionalArray;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LowerTriangularMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the row size: ");
int rowSize=Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the column size: ");
int columnSize=Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
int marr[][]=new int[rowSize][columnSize];
if(rowSize!=columnSize){
System.out.println("Since its not a square matrix,we can't find lower triangular matrix");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("Enter the array elements: ");
for(int i=0; i<rowSize; i++){
for(int j=0; j<columnSize; j++){
marr[i][j]=scanner.nextInt();
}
}
if(rowSize==columnSize){
System.out.println("Lower Triangular Matrix: ");{
for(int i=0;i<rowSize;i++){
for(int j=0;j<columnSize;j++){
if(j>i){
marr[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<rowSize;i++){
for(int j=0;j<columnSize; j++){
System.out.print(marr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}Output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.public class TwoDArray1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
// row wise printing.
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("row %d: ",i);
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.printf((a[i][j])+"\t");
}
}
// column-wise printing.
System.out.println("\n");
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("column %d: ",j);
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.printf((a[i][j])+"\t");
}
}
}
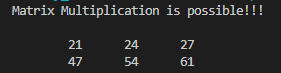
}2.public class MatrixMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][]={{1,2},{3,4}};
int b[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int productMatrix[][]=new int[2][3];
if(a[0].length==b.length){
System.out.println("Matrix Multiplication is possible!!!");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.println();
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
productMatrix[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
productMatrix[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
System.out.print("\t"+productMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Matrix Multiplication is not possible");
}
}
}3.import java.util.Scanner;
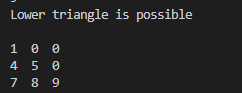
public class LowerTriangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows.. ");
int rows=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns.. ");
int col=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int a[][]=new int[rows][col];
System.out.println("Enter the values");
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++) {
System.out.println();
for(int j=0;j<col;j++) {
a[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
}
if(rows==col){
System.out.println("Lower triangle is possible");
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
if(j>i)
a[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
for(int []c:a){
System.out.println();
for(int d:c){
System.out.print(d+" ");
}
}
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
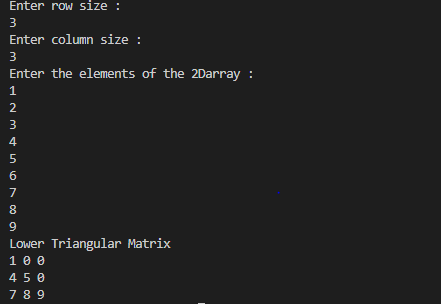
TASK-MULTI DIMENSIONAL ARRAY1.TwoDimensional1.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
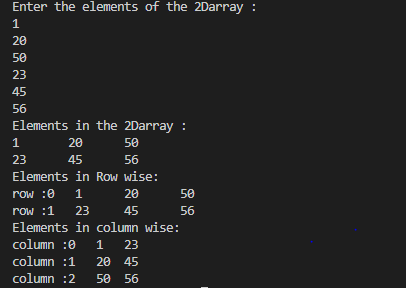
public class TwoDimensional1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr1[] []=new int[2][3];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the 2Darray :");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
arr1[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Elements in the 2Darray :");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr1[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Elements in Row wise:");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
System.out.print("row :"+i+" ");
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr1[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Elements in column wise:");
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
System.out.print("column :"+j+" ");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr1[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}Output2.MultiDimensional2.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
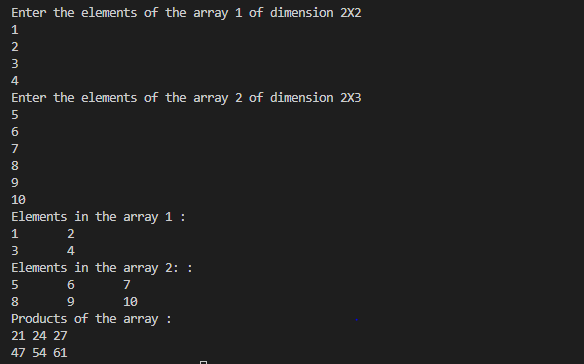
public class TwoDimensional2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr1[] []=new int[2][2];
int arr2[] []=new int[2][3];
int product[] []=new int[2][3];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array 1 of dimension 2X2 ");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<2; j++)
{
arr1[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array 2 of dimension 2X3 ");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
arr2[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Elements in the array 1 :");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<2; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr1[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Elements in the array 2: :");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr2[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Products of the array :");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
product[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
{
product[i][j]+=arr1[i][k]*arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(product[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output3.TriangularMatrix.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TriangularMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter row size :");
int rowSize=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter column size :");
int columnSize=sc.nextInt();
int arr[] []=new int[rowSize][columnSize];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the 2Darray :");
for(int i=0; i<rowSize; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<columnSize; j++)
{
arr[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
if(rowSize!=columnSize)
System.out.println("Matrix should be Square Matrix..");
System.out.println("Lower Triangular Matrix ");
for(int i=0;i<rowSize;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<columnSize; j++)
{
if(j>i)
{
arr[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<rowSize;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<columnSize; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.public class MultiDimAr1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {
{ 5, 6, 7 },
{ 8, 9, 10 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print("row " + i + ": ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print("col " + j + ": ");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output2.public class MatrixMult {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = {
{ 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 }
};
int b[][] = {
{ 5, 6, 7 },
{ 8, 9, 10 },
};
int m = a.length;
int n = a[0].length;
int p = b.length;
int q = b[0].length;
if (n == p) {
System.out.println("multiplication is possible");
int c[][] = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
c[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
c[i][j] = c[i][j] + (a[i][k] * b[k][j]);
}
}
}
System.out.println("after multiplication");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("multiplication is not possible");
}
}
}Output3.public class LowerTrianMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
int rows = a.length;
int cols1 = a[0].length;
int cols2 = a[1].length;
int cols3 = a[2].length;
if (rows == cols1 && rows == cols2 && rows == cols3) {
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
if (j > i) {
System.out.print("0 ");
} else {
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("the lower triangular matrix needs to be a square matrix");
}
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
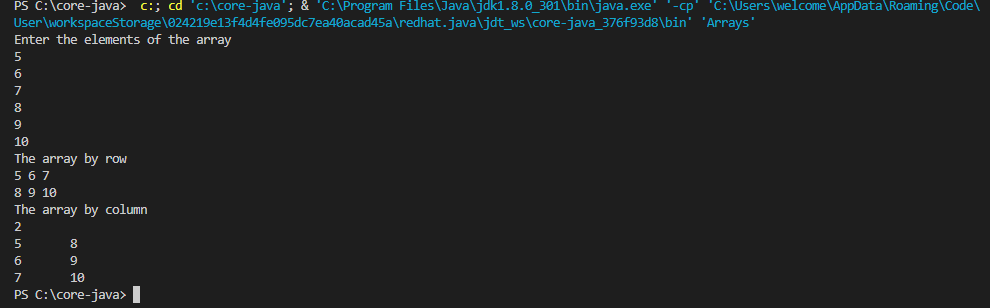
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array");
int array[][]=new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i<2;i++){
for (int j = 0; j<3;j++){
array[i][j] =scanner.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("The array by row");
for (int[] row: array){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The array by column");
System.out.println(array.length);
for(int i = 0; i < array[0].length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[j][i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
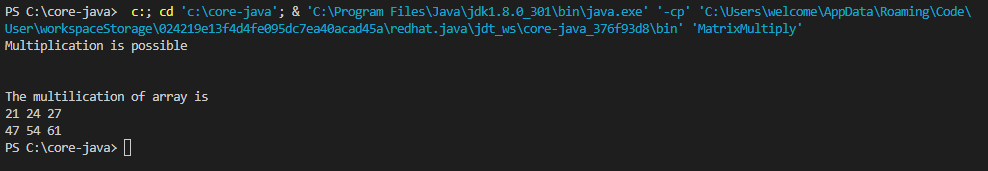
}Output:2public class MatrixMultiply {
public static void main(String[] args){
int array1[][]={{1,2},{3,4}};
int array2[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int array3[][]=new int[2][3];
if((array1[0].length)==array2.length){
System.out.println("Multiplication is possible");
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<3; j++){
for(int k=0; k<2; k++){
array3[i][j] += (array1[i][k])*(array2[k][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The multilication of array is");
for (int[] row: array3){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
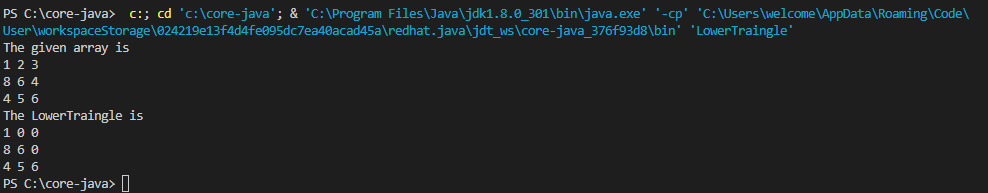
}Output:3public class LowerTraingle {
public static void main(String[] args){
int array[][]={{1,2,3},{8,6,4},{4,5,6}};
System.out.println("The given array is");
for (int[] row: array){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i=0; i<3; i++){
for (int j=0; j<3; j++){
if(j>i){
array[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The LowerTraingle is");
for (int[] row: array){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the first array size");
int sizeOne = obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the second array size");
int sizeTwo = obj.nextInt();
int array[][] = new int[sizeOne][sizeTwo];
for(int row=0;row<sizeOne;row++)
{
for(int column=0;column<sizeTwo;column++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the array element ");
int element = obj.nextInt();
array[row][column] = element;
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
for(int row=0;row<sizeOne;row++)
{
System.out.print("row:"+row);
for(int column=0;column<sizeTwo;column++)
{
System.out.print("\t"+ array[row][column]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
for(int row=0;row<sizeTwo;row++)
{
System.out.print("row:"+row);
for(int column=0;column<sizeOne;column++)
{
System.out.print("\t"+ array[column][row]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}2import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
int arrayOne[][] = new int[2][2];
int arrayTwo[][] = new int[2][3];
int arrayThree[][] = new int[2][3];
for(int row=0;row<2;row++)
{
for(int column=0;column<2;column++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the array element ");
int element = obj.nextInt();
arrayOne[row][column] = element;
}
}
for(int row=0;row<2;row++)
{
for(int column=0;column<3;column++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the array element ");
int element = obj.nextInt();
arrayTwo[row][column] = element;
}
}
int temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
{
arrayThree[i][j]+=arrayOne[i][k]*arrayTwo[k][j];
}
}
}
for(int row=0;row<2;row++)
{
for(int column=0;column<3;column++)
{
System.out.print("\t"+arrayThree[row][column]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}3import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the rows");
int rowLength = obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the rows");
int columnLength = obj.nextInt();
if (rowLength == columnLength) {
int arrayOne[][] = new int[rowLength][columnLength];
for (int row = 0; row < rowLength; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < columnLength; column++) {
System.out.println("Enter the array element ");
int element = obj.nextInt();
arrayOne[row][column] = element;
}
}
for (int row = 0; row < columnLength; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < columnLength; column++) {
if (column > row) {
arrayOne[row][column] = 0;
}
}
}
for (int row = 0; row < rowLength; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < columnLength; column++) {
System.out.print("\t" + arrayOne[row][column]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
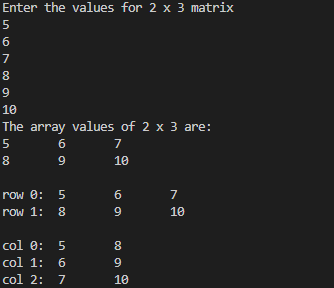
1tdayarray.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class tdayarray {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[][]=new int[2][3];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the values for 2 x 3 matrix");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
a[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
}
System.out.println("The array values of 2 x 3 are:");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("row %d:\t",i));
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("%d\t",a[i][j]));
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("col %d:\t",i));
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("%d\t",a[j][i]));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Output2matmul.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
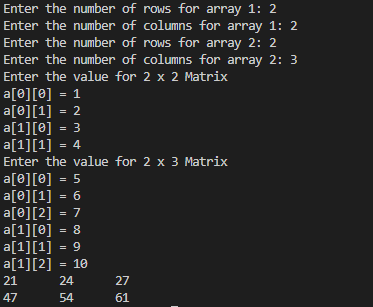
public class matmul {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows for array 1: ");
int rows=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the number of columns for array 1: ");
int columns=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows for array 2: ");
int rows1=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the number of columns for array 2: ");
int columns1=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int a[][]=new int[rows][columns];
int a1[][]=new int[rows1][columns1];
if(columns==rows1)
{
System.out.println(String.format("Enter the value for %d x %d Matrix",rows,columns));
int a2[][]=new int[rows][columns1];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("a[%d][%d] = ",i,j));
a[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
}
System.out.println(String.format("Enter the value for %d x %d Matrix",rows1,columns1));
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("a[%d][%d] = ",i,j));
a1[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
}
int sum=0,val;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
{
val=(a[i][k]*a1[k][j]);
sum=sum+val;
}
a2[i][j]=sum;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(a2[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else
{
System.out.print("Matrix multiplication can be done only if the number of columns in the the first array equals the number of rows in the second array.");
}
sc.close();
}
}Output3lower.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class lower {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
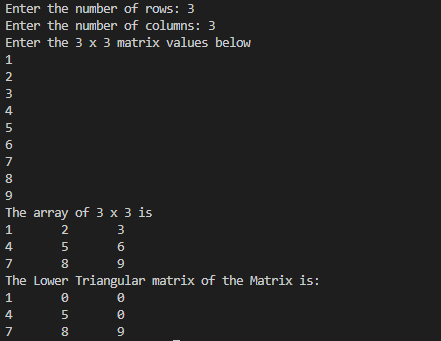
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows: ");
int rows=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the number of columns: ");
int columns=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
if(rows==columns)
{
System.out.println(String.format("Enter the %d x %d matrix values below",rows,columns));
int a[][]=new int[rows][columns];
for(int i=0; i<rows; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<columns; j++)
{
a[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
}
System.out.println(String.format("The array of %d x %d is ",rows,columns));
for(int i=0; i<rows; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<columns; j++)
{
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The Lower Triangular matrix of the Matrix is:");
for(int i=0; i<rows; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<columns; j++)
{
if(j>i)// if column value is greater than row then value should be 0
a[i][j]=0;
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Should be a square Matrix");
}
sc.close();
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1public class ArrayOp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {{ 5, 6, 7 },{ 8, 9, 10 }};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print("Arranging by row " + i + ": ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print("Arranging by column " + j + ": ");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2public class ArrayMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
int array1[][]={{1,2},{3,4}};
int array2[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int array3[][]=new int[2][3];
if((array1[0].length)==array2.length){
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<3; j++){
for(int k=0; k<2; k++){
array3[i][j] += (array1[i][k])*(array2[k][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The Multiplication of array is");
for (int[] row: array3){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}3public class LowerTriagularMatrix{
public static void main(String[] args){
int array[][]={{1,2,3},{8,6,4},{4,5,6}};
for (int i=0; i<3; i++){
for (int j=0; j<3; j++){
if(j>i){
array[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The Lower Triangle is");
for (int[] row: array){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1public class TwoDimensional {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {{ 5, 6, 7 },{ 8, 9, 10 }};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print("Row " + i + ": ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print("Column " + j + ": ");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2public class MultiDimensional {
public static void main(String[] args){
int arr1[][]={{1,2},{3,4}};
int arr2[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int arr3[][]=new int[2][3];
if((arr1[0].length)==arr2.length){
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<3; j++){
for(int k=0; k<2; k++){
arr3[i][j] += (arr1[i][k])*(arr2[k][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The Result Array is");
for (int[] row: arr3){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}3public class LowerTriangle{
public static void main(String[] args){
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{8,6,4},{4,5,6}};
for (int i=0; i<3; i++){
for (int j=0; j<3; j++){
if(j>i){
arr[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The Lower Triangle is");
for (int[] row: arr){
for (int num: row){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.class MainClass{
public static void main(String args[]){
int array1[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.print("row "+i+" : ");
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print( array1[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
int row = array1.length;
int column = array1[0].length;
int[][] transpose = new int[column][row];
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
transpose[j][i] = array1[i][j];
}
}
for(int[] rows : transpose) {
for (int columns : rows) {
System.out.print( columns + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}2.public class MainClass{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[][]={{1,2},{3,4}};
int b[][]={{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int c[][]=new int[3][3];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++)
{
c[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
System.out.print(c[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}3.public class MainClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int rows, cols;
int a[][] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{8, 6, 4},
{4, 5, 6}
};
rows = a.length;
cols = a[0].length;
if(rows != cols){
System.out.println("Matrix should be a square matrix");
}
else {
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix: ");
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
if(j > i)
System.out.print("0 ");
else
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1public class MultiDimensionArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] multi = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
multi[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.printf("row %d\t:", i);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", multi[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.printf("column %d\t:", i);
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", multi[j][i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
scanner.close();
}
}2public class MatrixMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.err.println("Enter array one");
int[][] multi1 = new int[2][2];
int[][] multi2 = new int[2][3];
int[][] result = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
multi1[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
System.err.println("Enter array two");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
multi2[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
result[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
result[i][j] += multi1[i][k] * multi2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(result[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
scanner.close();
}
}
3public class LowerTraingularMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.err.println("Enter array one");
System.out.println("Enter row ");
int row = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter column");
int column = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] result = new int[row][column];
if (row != column) {
System.out.println("Not a traingular matrix");
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
result[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
if (row != column) {
System.out.println("Not a traingular matrix");
} else {
System.out.println("Lower traingular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
if (j > i) {
result[i][j] = 0;
System.out.print(result[i][j] + "\t");
} else {
System.out.print(result[i][j] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
scanner.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
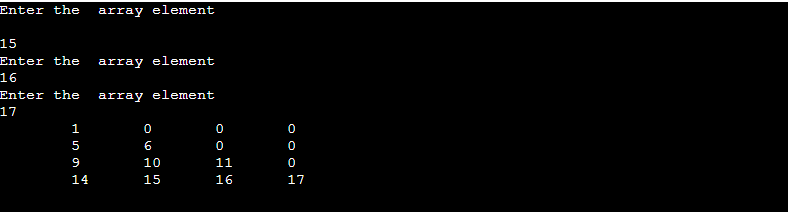
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[][] = new int [10][10];
System.out.println("Enter the number of row and column:");
int r=sc.nextInt();
int c=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(int i=0; i<r; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c; j++){
a[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i=0; i<r; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c; j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for(int i=0; i<c; i++){
for(int j=0; j<r; j++){
System.out.print(a[j][i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}2import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[][] = new int [10][10];
int b[][] = new int [10][10];
int prd[][] = new int [10][10];
System.out.println("Enter the number of row and column for First table:");
int r1=sc.nextInt();
int c1=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(int i=0; i<r1; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c1; j++){
a[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i=0; i<r1; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c1; j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Enter the number of row and column for Second table:");
int r2=sc.nextInt();
int c2=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(int i=0; i<r2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c2; j++){
b[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i=0; i<r2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c2; j++){
System.out.print(b[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
if (c1!=r2){System.out.println("column of first table should be equal to row of second table for matrix multiplication...");sc.close(); return ;}
for(int i=0; i<r1; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c2; j++){
prd[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0; k<r1; k++){
prd[i][j]+=a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
System.out.print(prd[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}3import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[][] = new int [10][10];
System.out.println("Enter the number of row and column:");
int r=sc.nextInt();
int c=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the elements:");
for(int i=0; i<r; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c; j++){
a[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i=0; i<r; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c; j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0; i<r; i++){
for(int j=0; j<c; j++){
if (j>i){
a[i][j]=0;
}
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1class RowColArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Row wise %d: ",i);
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.printf(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
}
System.out.println("\n");
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Column wise %d: \n",j);
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i][j]+"\t ");
}
}
}
}2class ProductArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr1[][] = {{1,2},{3,4}};
int arr2[][] = {{5,6,7},{8,9,10}};
int product[][] = new int[2][3];
System.out.println("Product of two arrays : ");
if(arr1[0].length == arr2.length){
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
product[i][j] = 0;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
product[i][j] += arr1[i][k]*arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.printf(product[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Multiplication is not possible...");
}
}
}3public class DimensionalArrayZero{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {{1,2,3},{8,6,4},{4,5,6}};
if(arr.length == arr[0].length){
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix is : ");
for(int i =0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j =0;j<arr[0].length;j++){
if(j>i){
System.out.print("0 ");
}
else{
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Matrix should be a square matrix...");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class d90 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
q1();
q2();
q3();
}
public static void q1() {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array");
int array[][] = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
array[i][j] = obj.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("The array by row");
for (int[] row : array) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The array by column");
System.out.println(array.length);
for (int i = 0; i < array[0].length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[j][i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void q2() {
int array1[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
int array2[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
int array3[][] = new int[2][3];
if ((array1[0].length) == array2.length) {
System.out.println("Multiplication is possible");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
array3[i][j] += (array1[i][k]) * (array2[k][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("The multilication of array is");
for (int[] row : array3) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public static void q3() {
int array[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 8, 6, 4 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
System.out.println("The given array is");
for (int[] row : array) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (j > i) {
array[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The LowerTraingle is");
for (int[] row : array) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
public class discussion90 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
tak1(a);
int arr1[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
int arr2[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
task2(arr1, arr2);
task3();
}
private static void task3() {
int arr3[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
int rows = arr3.length;
int cols1 = arr3[0].length;
int cols2 = arr3[1].length;
int cols3 = arr3[2].length;
if (rows == cols1 && rows == cols2 && rows == cols3) {
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < arr3.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr3[i].length; j++) {
if (j > i) {
System.out.print("0 ");
} else {
System.out.print(arr3[i][j] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("the lower triangular matrix needs to be a square matrix");
}
}
private static void task2(int[][] arr1, int[][] arr2) {
int productArray[][] = new int[2][3];
if (arr1[0].length == arr2.length) {
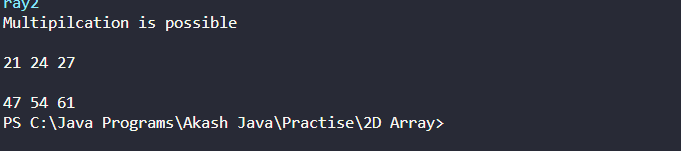
System.out.println("Multipilcation is possible");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
productArray[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
productArray[i][j] += arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(productArray[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
private static void tak1(int[][] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("row: %d", i);
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(" " + a[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.printf("column: %d", j);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print(" " + a[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Switch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
System.out.println("Row-Wise");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Column-Wise");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j][i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2import java.util.Scanner;
public class Switch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
int b[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
int productArray[][] = new int[2][3];
if (a[0].length == b.length) {
System.out.println("Multipilcation is possible");
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
productArray[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
productArray[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
System.out.print(productArray[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}3public class LowerTriangular {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (j > i) {
a[i][j] = 0;
}
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//2D array
int arr[][] = new int[2][3];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print("row" + i + ":\t");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print("column " + j + ":\t");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
//Write a program to multiply two 2-dimensional arrays, one by the other
int arr1[][] = new int[2][2];
int arr2[][] = new int[2][3];
int c[][] = new int[2][3];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the 1st array");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
arr1[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the 2nd array");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
c[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
c[i][j] += arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Lower triangular matrix
int a[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
int rows = a.length;
int cols1 = a[0].length;
int cols2 = a[1].length;
int cols3 = a[2].length;
if (rows == cols1 && rows == cols2 && rows == cols3) {
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
if (j > i) {
System.out.print("0 ");
} else {
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("the lower triangular matrix needs to be a square matrix");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class task90 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
p1();
p2();
p3();
}
public static void p1() {
int arr[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println();
System.out.print("row" + i + ":");
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print("\t" + arr[i][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.println();
System.out.print("column" + j + ":");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.print("\t" + arr[i][j]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void p2() {
int arr1[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
int arr2[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
int prod[][];
prod = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
prod[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
prod[i][j] = prod[i][j] + arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(prod[i][j] + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void p3() {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter no of rows");
int rows = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter no of columns");
int cols = scn.nextInt();
int arr[][] = new int[rows][cols];
System.out.println("enter the values of array");
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
arr[i][j] = scn.nextInt();
}
}
if (rows == cols) {
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (j > i) {
arr[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr ={{5, 6, 7}, {8, 9, 10}};
System.out.println("printing by row");
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
System.out.print("row " + i + ":");
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " \t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Printing by column");
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
System.out.print("col" + i + ":");
for(int j = 0; j < 2; j++){
System.out.print(arr[j][i] + " \t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
2import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr1[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
int arr2[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
int r1 = arr1.length;
int c1 = arr1[0].length;
int r2 = arr2.length;
int c2 = arr2[0].length;
if(c1 != r2){
System.out.println("Cannot multiply");
System.exit(0);
}
int[][] res = new int[2][3];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
res[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
res[i][j] += arr1[i][k] * arr2[k][j];
}
System.out.print(res[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
3import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
int rlength = arr.length;
int c1Length = arr[0].length;
int c2Length = arr[1].length;
int c3Length = arr[2].length;
if (rlength == c1Length && rlength == c2Length && rlength == c3Length) {
System.out.println("Lower triangular matrix");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
if (j > i) {
System.out.print("0 ");
} else {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} else {
System.out.println("Need to be a Square matrix");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code1public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = { { 5, 6, 7 }, { 8, 9, 10 } };
System.out.println("row");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("column");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j][i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code1import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int [][] arr = new int[2][3];
arr[0][0]=5;
arr[0][1]=6;
arr[0][2]=7;
arr[1][0]=8;
arr[1][1]=9;
arr[1][2]=10;
int a=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print("row "+a+": ");
for(int j=0;j<arr[0].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
a++;
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//question 2
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int [][] arr = new int[2][3];
arr[0][0]=5;
arr[0][1]=6;
arr[0][2]=7;
arr[1][0]=8;
arr[1][1]=9;
arr[1][2]=10;
int a=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr[0].length;i++){
System.out.print("col "+a+": ");
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[j][i]+" ");
}
a++;
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.



Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Write a program that declares a 2 x 3 array with the following values:
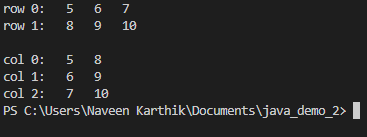
Print the array row-by-row, so your output looks like this:
Then print the array column-by-column, so your output looks like this:
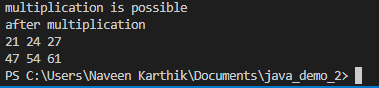
Write a program to multiply two 2-dimensional arrays, one by the other. This is called matrix multiplication. For example, if firstArray ( a 2 x 2 array) contains
and secondArray (a 2 x 3 array) appears as
then the product matrix is
productMatrix(0,0) = 1 * 5 + 2 * 8
productMatrix(1,0) = 3 * 5 + 4 * 8
productMatrix(0,1) = 1 * 6 + 2 * 9
productMatrix(1,1) = 3 * 6 + 4 * 9
productMatrix(0,2) = 1 * 7 + 2 * 10
productMatrix(1,2) = 3 * 7 + 4 * 10
Matrix multiplication can be done only if the number of columns in the multiplicand (the first array) equals the number of rows in the multiplier (the second array).
The program should read in the two arrays (or declare them and initialize them in the program), test to see if the multiplication is possible, and then multiply them if it is. The output will be a printout of the two arrays and will either output the product array or print a message saying that multiplication is not possible.
Hint: In order to perform the multiplication you need a loop nested in a loop nested in a loop. Yikes!
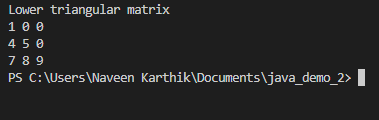
Lower triangular matrix is a square matrix in which all the elements above the principle diagonal will be zero. To find the lower triangular matrix, a matrix needs to be a square matrix that is, the number of rows and columns in the matrix need to be equal. Dimensions of a typical square matrix can be represented by n x n.
Consider the above example, principle diagonal element of given matrix is (1, 6, 6). All the elements above the diagonal needs to made zero. In our example, those elements are at positions (1, 2), (1, 3) and (2, 3). To convert given matrix into the lower triangular matrix, loop through the matrix and set the values of the element to zero where column number is greater than row number.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions