Task - Arrays - Single-dimensional Arrays #89
Replies: 55 comments
-
1,2public class PrintArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements of array");
for (int array : arr) {
System.out.println(array);
}
System.out.println("ENter number to find in array");
int find = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == find) {
System.out.println("element is found " + arr[i]);
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}3public class NumberTypesArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[] = new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int positive = 0;
int negative = 0;
int zero = 0;
int odd = 0;
int even = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
positive++;
}
if (arr[i] < 0) {
negative++;
}
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0) {
even++;
} else {
odd++;
}
if (arr[i] == 0) {
zero++;
}
}
System.out.println("positive num: " + positive);
System.out.println("negative num: " + negative);
System.out.println("odd num: " + odd);
System.out.println("even num: " + even);
System.out.println("zero num: " + zero);
scanner.close();
}
}4public class ArrayCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[] = new int[10];
int copy[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int j = copy.length;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (j >= 0) {
copy[j - 1] = arr[i];
j--;
}
}
System.out.println("reverse array : ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(copy[i]);
}
scanner.close();
}
}5public class ArraySumProduct {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum = sum + arr[i];
product = product * arr[i];
}
System.out.println("sum of array : " + sum);
System.out.println("product of array : " + product);
scanner.close();
}
}6public class MaxMinArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num;
System.out.println("Enter array size ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[num];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int max = 0;
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("max element is " + max + " min element is " + min);
scanner.close();
}
}7public class MaxMinDifference {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num;
System.out.println("Enter array size ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[num];
int maxdiff = 0;
int mindiff = 0;
int value = 0;
int maxindex1 = 0;
int maxindex2 = 0;
int minindex1 = 0;
int minindex2 = 0;
int count = 0;
System.out.println("enter value ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (i != j) {
if (count < 1) {
value = arr[i] - arr[j];
value = Math.abs(value);
count++;
maxindex1 = i;
maxindex2 = j;
minindex1 = i;
minindex2 = j;
maxdiff = value;
mindiff = value;
}
value = Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[j]);
if (maxdiff < value) {
maxdiff = value;
maxindex1 = i;
maxindex2 = j;
}
if (mindiff > value) {
mindiff = value;
minindex1 = i;
minindex2 = j;
}
}
}
}
System.out.printf("Maximum number addition of pair %d and %d is %d\n", arr[maxindex1], arr[maxindex2], maxdiff);
System.out.printf("Maximum number difference of pair %d and %d is %d", arr[minindex1], arr[minindex2],
mindiff);
scanner.close();
}
}8public class SubArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num;
System.out.println("Enter array size ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[num];
int sub1 = 3;
int sub2 = 8;
int subArray[] = new int[3];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int j = 0;
if (arr.length > sub2) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i > sub1 && i < sub2 && j < sub1) {
subArray[j] = arr[i];
j++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("SubArray: ");
for (int i = 0; i < subArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println(subArray[i]);
}
scanner.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
for(int arrayStart=0;arrayStart<storedArray.length;arrayStart++)
{
System.out.println("Array:"+arrayStart+" value:"+storedArray[arrayStart]);
}
}
}2import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
System.out.println("Enter the stored number:");
int inputStoredNumber=obj.nextInt();
boolean flag=false;
for(int arrayIterate=0;arrayIterate<storedArray.length;arrayIterate++)
{
if(storedArray[arrayIterate]==inputStoredNumber)
{
System.out.println("your input number is there in this array");
flag=true;
}
}
if(flag==false)
{
System.out.println("you number is not stored in this array");
}
}
}3import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[20];
for(int i=0;i<20;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
int positiveNumbers=0;
int negativeNumbers=0;
int oddNumbers=0;
int evenNumbers=0;
int zeros=0;
for(int arrayIterate=0;arrayIterate<storedArray.length;arrayIterate++)
{
if(storedArray[arrayIterate]>0)
{
positiveNumbers++;
}else if(storedArray[arrayIterate]<0)
{
negativeNumbers++;
}else
{
zeros++;
}
if(storedArray[arrayIterate]!=0)
{
if(storedArray[arrayIterate]%2==0)
{
evenNumbers++;
}else{
oddNumbers++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("positive numbers: "+positiveNumbers);
System.out.println("negative numbers: "+negativeNumbers);
System.out.println("zeros: "+zeros);
System.out.println("even numbers: "+evenNumbers);
System.out.println("odd numbers: "+oddNumbers);
}
}4import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[10];
int []copiedArray=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
int j=0;
for(int k=storedArray.length-1;k>0;k--)
{
copiedArray[j]=storedArray[k];
j++;
}
System.out.println("after copied array :");
for(int arrayIterate=0;arrayIterate<copiedArray.length;arrayIterate++)
{
System.out.print(copiedArray[arrayIterate]+"\t");
}
}
}5import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[5];
int sum=0;
int product=1;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
for(int arrayIterate=0;arrayIterate<storedArray.length;arrayIterate++)
{
sum+=storedArray[arrayIterate];
product*=storedArray[arrayIterate];
}
System.out.println("sum: "+sum);
System.out.println("product: "+product);
obj.close();
}
}6import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
int small=storedArray[0];
int big=storedArray[0];
for(int arrayIterate=0;arrayIterate<storedArray.length;arrayIterate++)
{
if(big<storedArray[arrayIterate])
{
big=storedArray[arrayIterate];
}
if(small>storedArray[arrayIterate])
{
small=storedArray[arrayIterate];
}
}
System.out.println("greatest number: "+big);
System.out.println("smallest number: "+small);
obj.close();
}
}7import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] storedArray = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Enter the input number " + i);
int input = obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i] = input;
}
int max = 0;
int min = 0;
int temp = 0;
int temp1 = 1;
boolean flag = false;
int maxNumber1 = 0;
int maxNumber2 = 0;
int minNumber1 = 0;
int minNumber2 = 0;
for (int arrayIterate = 0; arrayIterate < storedArray.length; arrayIterate++) {
for (int index = 0; index < storedArray.length; index++) {
if (arrayIterate != index) {
max = storedArray[index] - storedArray[arrayIterate];
if (max >= temp) {
temp = storedArray[index] - storedArray[arrayIterate];
maxNumber1 = storedArray[index];
maxNumber2 = storedArray[arrayIterate];
}
min = storedArray[index] - storedArray[arrayIterate];
if (min > 0) {
if (flag == false) {
temp1 = storedArray[index] - storedArray[arrayIterate];
flag = true;
}
if (min <= temp1) {
temp1 = storedArray[index] - storedArray[arrayIterate];
minNumber1 = storedArray[index];
minNumber2 = storedArray[arrayIterate];
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("maximum pair number1: " + maxNumber1 + ", number2: " + maxNumber2 + " value is: " + temp);
System.out.println("minimum pair number1: " + minNumber1 + ", number2: " + minNumber2 + " value is: " + temp1);
obj.close();
}
}8import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
int []storedArray=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the input number "+i);
int input=obj.nextInt();
storedArray[i]=input;
}
System.out.println("Enter the start elementing element of an array ");
int startArray=obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the ending element of an array ");
int endArray=obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("The sub array is: ");
for(int arrayIterate=(startArray-1);arrayIterate<(endArray-1);arrayIterate++)
{
System.out.print(storedArray[arrayIterate]+"\t");
}
obj.close();
}
}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1_UserInputpackage Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UserInputProb1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10]; // array declaration
System.out.println("Enter 10 elements: ");
//to get input from user
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
System.out.print("The Array Elements are: ");
//printing array elements
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}2_CheckNumberpackage Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CheckNumberProb2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10]; //array declaration
System.out.println("Enter 10 elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
System.out.println("Enter a number to check: ");
int check=Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
Arrays.sort(arr); //sorting array by using Arrays class
int checkResult=Arrays.binarySearch(arr,check); //using binarysearch method in Arrays class
boolean printResult=checkResult>0?true:false;
System.out.println(check+" present in the array: "+printResult);
sc.close();
}
}3_ArrayOperationpackage Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OperationInArrayProb3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int positiveCheck=0,negativeCheck=0,oddNumberCheck=0,evenNumberCheck=0,zero=0,i;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter 20 elements: ");
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
if(arr[i]>0){ //check for positive number
positiveCheck++;
}
else if(arr[i]<0){ //check for negative number
negativeCheck++;
}
else{ //check for zero
zero++;
}
if(arr[i]%2==0){ //check for even numbers
evenNumberCheck++;
}
else{
oddNumberCheck++; //check for odd numbers
}
}
System.out.print("Number of positive numbers: "+positiveCheck+"\nNumber of negative numbers: "+negativeCheck+"\nNumber of odd numbers: "+oddNumberCheck+"\nNumber of even numbers: "+evenNumberCheck+"\nNumber of Zero: "+zero);
sc.close();
}
}4_ReversedArraypackage Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseArrayProb4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int [] arr1=new int[10];
int [] arr2=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements: ");
for(int i=0; i<arr1.length; i++){
arr1[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int j=0;
for(int i=arr2.length-1; i>=0; i--){ //reversing an array
arr2[i]=arr1[j];
j++;
}
System.out.println("Reversed Array: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr2.length; i++){ //printing reversed array
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}5_SumProductArraypackage Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SumProductArrayProb5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int sum=0,product=1;
System.out.println("Enter the number of array elements:"); //getting the size of array from user
int num=sc.nextInt();
int[] a=new int[num];
System.out.println("Enter the array elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ //condition for sum and product
sum=sum+a[i];
product=product*a[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of array elements is: "+sum);
System.out.println("Product of array elements is: "+product);
sc.close();
}
}6_MaxMinArraypackage Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxMinArrayProb6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter any 10 elements in the array: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
int max=arr[0];
int min=arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ // to find largest element in an array condition
if(arr[i]>max){
max=arr[i];
}
if(arr[i]<min){ //to find smallest element in an array
min=arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Largest element of an array is "+max+"\nSmallest element of an array is "+min);
sc.close();
}
}7_MinMaxDifferencePairpackage Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxMinDiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int ep1=0,ep2=0,ep3=0,ep4=0;
System.out.print("Enter the number of array elements:");
int num=sc.nextInt();
int[] arr=new int[num];
System.out.println("Enter the array elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(arr); //sort using Arrays class
int maxDiff=arr[1]-arr[0];
int minDiff=arr[1]-arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++){ //find max space elements pair
if(maxDiff<(arr[j]-arr[i])){
maxDiff = arr[j]-arr[i];
ep1=i;
ep2=j;
}
if((arr[i]-arr[j])>minDiff) //find min space elements pair
minDiff=arr[i]-arr[j];
ep3=i;
ep4=j;
}
}
System.out.println("The maximum difference among elements: "+Math.abs(maxDiff)+" and the maximum differencec element pair is: "+ep1+" & "+ep2);
System.out.println("The minimum difference among elements: "+Math.abs(minDiff)+" and the minimum differencec element pair is: "+ep3+" & "+ep4);
sc.close();
}
}8_SubArraypackage Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SubArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={10, 12, 20, 30, 25, 40, 32, 31, 35, 50, 60};
int[] subArray = Arrays.copyOfRange(array,3,8); //subarray using copyOfRange method in Arrays class
System.out.println("Input Array: ");
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
System.out.print(array[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println("\nSubarray that lies between the indexes 3 and 8: "); //printing the subarray
for(int i=0;i<subArray.length;i++){
System.out.print(subArray[i] + " ");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
TASK-SINGLE DIMENSION ARRAY1.ArraysDemo.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArraysDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the array size : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter thr elements of an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements in an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
}2.ArraySearch.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class ArraySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n;
boolean found=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("NO OF ELEMENTS YOU WANT TO ENTER : ");
n=sc.nextInt();
int element;;
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("ENTER THE ELEMENTS");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("ENTER THE ELEMENTS YOU WANT TO SEARCH");
element=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]==element)
{
found=true;
System.out.println("ELEMENT IS PRESENT IN THE POSITION "+ (i+1));
break;
}
}
if(found==false)
{
System.out.println("ELEMENT IS NOT PRESENT");
}
}
}3.CountDemo.java4.ArrayReverse.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayReverse {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("ENTER 10 ELEMENTS");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("REVERSE ARRAY :");
for(int i=a.length-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int b[]=new int[a.length];
b[i]=a[i];
System.out.print(b[i]+" ");
}
}
}5.ArraySumProduct.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArraySumProduct {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int sum=0,product=1;
System.out.println("Enter the array size : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter thr elements of an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sum=sum+a[i];
product=product*a[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of array : "+sum);
System.out.println("Product of array : "+product);
sc.close();
}
}6.LargestSmallestArray.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class LargestSmallestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("NO OF ELEMENTS YOU WANT TO ENTER : ");
n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
int max=0;
System.out.println("ENTER THE ELEMENTS");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]>max) {
max=a[i];
}
}
System.out.println("LARGEST ELEMENT IN AN ARRAY IS "+max);
int min=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]<min) {
min=a[i];
}
}
System.out.println("SMALLEST ELEMENT IN AN ARRAY IS "+min);
}
}7.ArrayDifference.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayDifference {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the array size : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter thr elements of an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements in an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println("\nSorted array :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
int tmp = 0;
if (arr[i] > arr[j])
{
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
int max_diff = arr[1] - arr[0];
int i,j;
for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] - arr[i] > max_diff)
max_diff = arr[j] - arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("\nMaximum Difference : "+max_diff);
int min_diff = arr[1] - arr[0];
for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] - arr[i] < min_diff)
min_diff = arr[j] - arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Minimum Difference : "+min_diff);
}
}8.SubArray.javapackage Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SubArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the array size : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements in an array :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println("\nEnter the start index and the end index :");
int start_index=sc.nextInt();
int end_index=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Sub Arrays :");
for(int i=start_index;i<=end_index;i++) //for(int i=start_index;i<end_index;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements: ");
for( int i=0;i<10;i++){
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());//Getting inputs from the user.
}
System.out.println("The Elements are: ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.println(a[i]);// Printing the elements of the array.
sc.close();
}
}2.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the element to find: "); /*getting one element from the user
which is to be searched in the array */
int b=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(a[i]==b){ // Checks for the element in the array.
System.out.println("Element found!!!");
}
sc.close();
}
}
}3.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int countPositive=0;
int countNegative=0;
int countEven=0;
int countOdd=0;
int countZero=0;
int a[]=new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter the elements...");
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ // traversing the loop.
if(a[i]==0){ // Checks for number of zeroes.
countZero++;
}
if(a[i]>0){ // Checks for Positive number
countPositive++;
}
if(a[i]<0){ //Checks for Negative number.
countNegative++;
}
if(a[i]%2==0){ // Checks for Even number.
countEven++;
}
if(a[i]%2!=0){ // Checks for odd number.
countOdd++;
}
}
System.out.printf("countPositive=%d\ncountNegative=%d\ncountOdd=%d\ncountEven=%d\ncountZero=%d",countPositive,countNegative,countOdd,countEven,countZero);
sc.close();
}
}4.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
int b[]=new int[10]; // Initializing another array
int j=0;
System.out.println("Enter the elements!!!");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=9;i>=0;i--){ // travering array a in reverse order.
b[j]=a[i]; // copying the elements of the array a to b.
j++;
}
System.out.println("The reversed elements are!!!");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.println(b[i]);
sc.close();
}
}
5.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[5];
int sum=0;
int product=1;
System.out.println("Enter the elements of an array: ");
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
sum=sum+a[i]; // Summation of elements.
product=product*a[i]; // Product of elements.
}
System.out.printf("The sum is %d and the product is %d",sum,product);
sc.close();
}
}6.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[5];
System.out.println("Enter the elements!!!");
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int min=a[0]; // Assuming minimum value.
int max=a[0]; // Assuming maximum value.
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
if(a[i]<min) // Assigning minimum value.
min=a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
if(a[i]>max) // Assigning maximum value.
max=a[i];
}
System.out.printf("The largest number is %d and Smallest number is %d",max,min);
sc.close();
}
}7.import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i=0,j=0;
System.out.println("Enter the number of elements");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the elements!!!");
for( i=0; i<n; i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a);
/*Assumption of initial values to the differences.*/
int maxDiff=0;
int minDiff=0;
int index1=0;
int index2=0;
int index3=0;
int index4=0;
for( i=0;i<n;i++){ // Iterating Variable 'i' for Array 'a'.
for( j=i+1;j<n;j++){ //Iterating Variable 'j' for Array 'a'
if(maxDiff<a[i]-a[j] || maxDiff<(a[j]-a[i])){ //Checks for the maxDifference by checking each value of array.
maxDiff=a[i]-a[j];
index1=i; //Assigning index values.
index2=j;
}
}
}
for( i=0;i<n;i++){
for( j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(minDiff>a[i]-a[j]){ //Checks for the minDifference by checking each value of array.
minDiff=a[i]-a[j];
index3=i;
index4=j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("The minimum difference pairs are %d and %d, maximum difference pairs are %d and %d",a[index1],a[index2],a[index3],a[index4]);
sc.close();
}
}8.import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of elements");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the elements!!!");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the StartingIndex"); // SubArray 0 index.
int startingIndex=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the EndingIndex"); // SubArray nth index.
int endingIndex=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("The sub-array elements are: ");
for(int i=startingIndex+1;i<endingIndex;i++){ // Traversing the SubArray.
System.out.println(a[i]+"\t");
}
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1,2public class StoringElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the no.of elements to store :: ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("The array elements are :: ");
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("Enter the element to check whether it is present in the array :: ");
int val = sc.nextInt();
for(int i : arr){
if(i == val){
b = true;
break;
}
}
if (b == true) {
System.out.println("Present in the array :: ");
} else {
System.out.println("Not present in the array :: ");
}
}
}3public class Numbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n,p=0,c=0,o=0,e=0,z=0;
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
n=sc.nextInt();
if (n>0) p++; //count of positive no's.
if (n<0) c++; //count of negative no's.
if (n%2==0) e++; //count of even no's.
if (n%2!=0) o++; //count of odd no's
if (n==0) z++; //count of zeros
}
System.out.println("no.of positive numbers"+p);
System.out.println("no.of negative numbers"+c);
System.out.println("no.of odd numbers"+o);
System.out.println("no. of even numbers"+e);
System.out.println("no.of zeroes"+z);
}
}4public class ReverseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array elements are ::");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("Reversed Array elements are ::");
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}5public class SumProduct {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[10];
int sum = 0, product = 1;
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
sum += arr[i];
product *= arr[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of the array :: " + sum);
System.out.println("Product of the array :: " + product);
}
}6public class LargestSmallest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the no.of elements to store :: ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[10];
int largest,smallest,i;
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
largest=smallest=arr[0];
for(i=1;i<arr.length;++i)
{
if(arr[i]>largest)
largest=arr[i];
if(arr[i]<smallest)
smallest=arr[i];
}
System.out.println("The smallest element is" + smallest);
System.out.println("The largest element is" + largest);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
/*Take 10 integer inputs from the user and store them in an array and print them on screen.*/
class Array1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the 10 integer inputs:");
int a[]= new int[10];
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a[i] = sc.nextInt(); // Store the array of values
}
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println(a[i]);// Printing the values stored
}
sc.close();
}
}2import java.util.Scanner;
/*Take 10 integer inputs from the user and store them in an array. Again ask the user to give a number. Now, tell the user whether that number is present in the array.*/
public class Array2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the 10 integer inputs:");
int a[]= new int[10];
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the Elements to find:");
int b=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
if(a[i]==b) //Matching elements caught from a
System.out.println(b+"\t is found");
}
sc.close();
}
}3import java.util.Scanner;
/*Take 20 integer inputs from the user and print the following:
number of positive numbers
number of negative numbers
number of odd numbers
number of even numbers
number of 0s. */
public class Array3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[20];
int countPositive=0;
int countNegative=0;
int countEven=0;
int countOdd=0;
int countZeroes=0;
int i;
System.out.println("Enter the 20 Integer numbers");
for( i=0; i<20; i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for( i=0; i<20; i++){
if(a[i]>0)
countPositive++;
if(a[i]<0)
countNegative++;
if(a[i]%2==0)
countEven++;
if(a[i]==0)
countZeroes++;
if(a[i]%2!=0)
countOdd++;
}
System.out.println("Positive numbers are "+countPositive);
System.out.println("Negative numbers are "+countNegative);
System.out.println("Odd numbers are "+countOdd);
System.out.println("Even numbers are "+countEven);
System.out.println("Zeros Present are "+countZeroes);
sc.close();
}
}4import java.util.Scanner;
/*Take 10 integer inputs from user and store them in an array. Now, copy all the elements in an another array but in reverse order.
*/
public class Array4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]= new int[10];
int j=0;
System.out.println("Enter 10 integer inputs");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int b[]= new int[10];
for(int i=9; i>=0; i--) { // Reverse traverse
b[j]=a[i]; //Assigning values to b array
j++;
}for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
System.out.println("reverse order "+b[i]);
sc.close();
}
}5import java.util.Scanner;
/*Write a program to find the sum and product of all elements of an array.
*/
public class Array5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]= new int[5],sum=0,product=1;
System.out.println("Enter a number of elements");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
sum+=a[i]; //Adding and storing in sum variable
product*=a[i]; // Product and storing in product variable
}
System.out.println("The Sum of the elements"+sum);
System.out.println("The Product of the elements"+product);
sc.close();
}
}6import java.util.Scanner;
/*Find the largest and smallest elements of an array.*/
public class Array6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]= new int[5];
System.out.println("Enter the inputs");
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int min=a[0],max=a[0]; // initialize min and max
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
if(a[i]<min){ //check for the min value
min=a[i]; //Assign the value
}
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
if(a[i]>max){ //check for max
max=a[i]; //Assign max
}
}
System.out.println(max+" Largest "+min+" Smallest");
sc.close();
}
}7import java.util.*;
/*Consider an integer array, the number of elements in which is determined by the user. The elements are also taken as input from the user. Write a program to find those pair of elements that has the maximum and minimum difference among all element pairs. */
class Array7{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the size of the array");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int j=0;
int a[] = new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the number of elements");
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a);
int max=0,min=0,index1=0,index2=0,index3=0,index4=0; //Initialize max,min and index values for two pairs
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
for(j=i+1; j<a.length; j++){
if(max<a[i]-a[j]){ //check for max difference
max=a[i]-a[j];
index1=i;
index2=j;}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
for(j=i+1; j<a.length; j++){
if(min>a[i]-a[j]){ //check for min difference
min=a[i]-a[j];
index3=i;
index4=j;
}
}}
System.out.printf("Minimum difference pairs %d %d and Maximum difference pairs %d %d",a[index3],a[index4],a[index1],a[index2]);
sc.close();
}
} 8import java.util.Scanner;
/*If the input array is [10, 12, 20, 30, 25, 40, 32, 31, 35, 50, 60], your program should be able to find that the subarray lies between the indexes 3 and 8.*/
public class Array8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]= new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 elements");
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int b[]= new int[4]; //sub array
int j=0;
for(int i=4; i<8;i++){ //Extracting the sub array from a array
b[j]=a[i]; //Storing the values from a
j++;
}
System.out.println("Sub array consists of :");
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
System.out.println(b[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1arr10.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class arr10 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[]=new int[10];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the 10 numbers below");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
int i=0;
while(i<10)
{
System.out.println(String.format("a[%d] = %d",i,a[i]));
i++;
}
sc.close();
}
}Output2check.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class check {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 numbers below");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
System.out.print("Enter the value to be searched:");
int val=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(val==a[i])
{
System.out.println(String.format("%d is present in the array",val));
break;
}
else
{
if(i==9)
{
System.out.println(String.format("%d is not present in the array",val));
}
}
}
sc.close();
}
}Output3.arr3.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class arr3 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter the 20 integers below:");
int i=0;
while(i<20)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
i++;
}
int neg=0,pos=0,even=0,odd=0,zero=0;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
if(a[i]<0)
{
neg++;
}
if(a[i]>0)
{
pos++;
}
if(a[i]%2==0 && a[i]>0)
{
even++;
}
if(a[i]%2!=0 && a[i]>0)
{
odd++;
}
if(a[i]==0)
{
zero++;
}
}
System.out.println(String.format("Positive values = %d\nNegative values = %d\nOdd values = %d\nEven values = %d\nNo. of Zero's=%d",pos,neg,odd,even,zero));
sc.close();
}
}Output4.revarr.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class revarr {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
int a1[]=new int[10];
int i=0;
while(i<10)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
i++;
}
int j=0;
i=9;
while(i>=0 && j<=10)
{
a1[j]=a[i];
i--;
j++;
}
System.out.println("Array values of array 1");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print(String.format(" %d\t",a[i]));
}
System.out.println();
for(i=9,j=0;i>=0&&j<10;i--,j++)
{
a1[j]=a[i];
}
System.out.println("Array values of array 2 copied from array 1");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print(String.format(" %d\t",a1[i]));
}
sc.close();
}
}Output5.sump.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class sump {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 numbers: ");
int sum=0;
int prod=1;
int i;
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
sum=sum+a[i];
prod=prod*a[i];
}
System.out.println(String.format("Sum = %d\nProduct =%d", sum,prod));
sc.close();
}
}Output6.grt.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class grt {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
int temp,j,i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<10;j++)
{
if(a[i]<a[j])
{
// a[i]=a[i];
}
else
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(String.format("%d is the greatest",a[9]));
System.out.println(String.format("%d is the smallest",a[0]));
sc.close();
}
}Output7.ques7.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class ques7 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i;
System.out.print("Enter the number of values to be entered: ");
int n=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int a[]=new int[n];
int mi[]=new int [n];
int temp;
int val1=0,val2=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
if(i==(n-1))
sc.close();
}
int j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)// sorting of array values
{
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i]>a[j])
{
a[i]=a[i];
}
else
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}
}
}
int max=0,min=0,max1,min1;// finding the difference of minimum and maximum among all the elements
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n-1;j++)
{
if(((j+i)+1)<n)
{
mi[j]=a[i]-a[(j+i)+1];
}
else
{
break;
}
}
min1=mi[0];
max1=mi[(n-1)-1-i];
if(max1>max )//checks with the previous max values that has been assigned from mi[] array and stores the
{
val1=a[i];
max=max1;
min=min1;//also stores the minimum value for further iterations
val2=a[i+1];
}
if(min1<=min)
{
val2=a[(i+1)-1];
min=min1;
}
}
System.out.print(String.format("The maximum and minimum of all the elements lies in (%d and %d) pairs\n Max = %d Min = %d ",val1,val2,max,min));
}
}output8.subarray.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class subarray {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number of values to be entered: ");
int n=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int ar[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the values below");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
System.out.println("The index value of the array ends at : "+(n-1));
System.out.print("Enter the starting range: ");
int start=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.print("Enter the Ending range: ");
int end=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
if(end>(n-1))
{
System.out.println("Enter the array value as per the end index value provided");
}
else if(start>(n-1))
{
System.out.println("The value is out of bound");
}
else
{
System.out.println("The subarray of "+start+" and "+end+" is ");
System.out.print("[");
for(int i=start;i<=end;i++)
{
System.out.print(String.format("%d",ar[i]));
if(i!=end)
{
System.out.print(",");
}
}
System.out.print("]");
}
sc.close();
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int ar[] = new int[10];
int c=1;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
System.out.println("Elements in array");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(ar[i]);
}
}
}2.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int c=1,i;
int ar[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
System.out.println("Enter another value to seqrch in array");
int nv=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int flag=0;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(ar[i]==nv)
{
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==1)
{
System.out.println("The number "+nv+" is present in the array");
}
else
{
System.out.println("The number "+nv+" is not present in the array");
}
}
}3.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 20 integer values");
int c=1,i;
int ar[] = new int[20];
int pn=0,nn=0,on=0,en=0,zero=0;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
if(ar[i]>0)
{
pn++;
}
if(ar[i]<0)
{
nn++;
}
if(ar[i]%2!=0)
{
on++;
}
if(ar[i]%2==0)
{
en++;
}
if(ar[i]==0)
{
zero++;
}
}
System.out.println("number of positive numbers: "+pn);
System.out.println("number of negative numbers: "+nn);
System.out.println("number of odd numbers: "+on);
System.out.println("number of even numbers: "+en);
System.out.println("number of 0s: "+zero);
}
}4.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int c=1,i,j;
int ar[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
int newar[] = new int[10];
j=9;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
newar[j]=ar[i];
j--;
}
System.out.println("Elements in new array");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(newar[i]);
}
}
}5.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int c=1,i;
int ar[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
int sum=0,prod=1;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sum += ar[i];
prod *= ar[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of elements in arrays: "+sum);
System.out.println("Product of elements in arrays: "+prod);
}
}6.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int c=1,i,j;
int ar[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+c+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine()); c++;
}
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<10;j++)
{
if(ar[i]>ar[j])
{
int t=ar[i];
ar[i]=ar[j];
ar[j]=t;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The smallest element in the array is "+ar[0]);
System.out.println("The largest element in the array is "+ar[9]);
}
}7.package javademo2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number of elements to be stored in an array");
int size = sc.nextInt();
int ar[] = new int[size];
int c=1,i,j;
int maxdiff=0,mindiff=0;
int i1=0,i2=0,i3=0,i4=0;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter element"+c+": ");
ar[i]=sc.nextInt(); c++;
}
Arrays.sort(ar);
System.out.println("given array elements");
for(int a : ar)
{
System.out.print(a+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<size;j++)
{
if(mindiff<ar[i]-ar[j])
{
mindiff=ar[i]-ar[j];
i1=i;
i2=j;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The pair of elements having minimum difference are: "+ar[i1]+" "+ar[i2]);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<size;j++)
{
if(maxdiff>ar[i]-ar[j])
{
maxdiff=ar[i]-ar[j];
i3=i;
i4=j;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The pair of elements having maximum difference are: "+ar[i3]+" "+ar[i4]);
}
}8.package javademo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Arrays8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter 10 integer values");
int i,j;
int ar[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.print("Enter value"+i+": ");
ar[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
int ar2[] = new int[4];
j=0;
for(i=4;i<8;i++)
{
ar2[j]=ar[i];
j++;
}
System.out.println("Sub array elements between the indexes 3 and 8 is ");
for(i=0;i<ar2.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(ar2[i]);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n=10;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int[] array = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 elements of the array: ");
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
array[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array elements are: ");
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
}
} 2import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] array = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 elements of the array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
array[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the element to find: ");
int search = sc.nextInt();
boolean check = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (array[i] == search) {
check = true;
System.out.println("Element found " + (i + 1));
break;
}
}
if (check == false) {
System.out.println("Element not found");
}
}
}3import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int positive=0,negative=0,odd=0,even=0,zero=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter 20 elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
if(arr[i]>0){
positive++;
}
else if(arr[i]<0){
negative++;
}
else{
zero++;
}
if(arr[i]%2==0){
even++;
}
else{
odd++;
}
}
sc.close();
System.out.println("Number of positive numbers: "+positive);
System.out.println("Number of negative numbers: "+negative);
System.out.println("Number of odd numbers: "+odd);
System.out.println("Number of even numbers: "+even);
System.out.println("Number of zeros: "+zero);
}
}4import java.util.Scanner; } 5import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 elements of the array: ");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0;
int prod = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum = sum + arr[i];
prod = prod * arr[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of all the elements of an array: " + sum);
System.out.println("Product of all the elements of an array: " + prod);
}
} 6import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println("Enter the 5 elements of the array: ");
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int smallest = arr[0];
int largest = arr[0];
for(int i=1; i< arr.length; i++)
{
if(arr[i] > largest)
largest = arr[i];
else if (arr[i] < smallest)
smallest = arr[i];
}
System.out.println("Smallest Number is : " + smallest);
System.out.println("Largest Number is : " + largest);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1,2,4import java.util.Scanner;
public class FindElement {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int array[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 array of elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array of elements:");
for (int i:array){
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("Enter the element to find:");
int element=scanner.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
if (array[i]==element){
System.out.println("The element find at index " + i);
break;
}
}
int AnotherArray[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("AnotherArray of elements in Reverse Order:");
for (int i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--){
AnotherArray[i]=array[i];
System.out.println(AnotherArray[i]);
}
}
}3import java.util.Scanner;
public class FindNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 20 elements of array:");
int elements[]=new int[20];
for(int i=0; i<20; i++){
elements[i]=scanner.nextInt();
}
int zero=0;
int negative=0;
int positive=0;
int evenNumber=0;
int oddNumber=0;
for(int i=0; i<elements.length; i++){
if(elements[i]==0){
zero++;
}
if(elements[i]<0){
negative++;
}
if(elements[i]>0){
positive++;
}
if(elements[i]%2==0){
evenNumber++;
}
else{
oddNumber++;
}
}
System.out.println("Number of Positive Numbers :"+positive);
System.out.println("Number of Positive Negative :"+negative);
System.out.println("Number of Positive EvenNumbers :"+evenNumber);
System.out.println("Number of Positive oddNumbers :"+oddNumber);
System.out.println("Number of Zeros :"+zero);
}
}5import java.util.Scanner;
public class SumAndProduct {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int array[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 array of elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int sum=0;
int product=1;
for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){
sum += array[i];
product *= array[i];
}
System.out.println("The sum of array elemnts :"+sum);
System.out.println("The product of array elements :"+product);
}
}6import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxMin {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int array[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 array of elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array of elements:");
for (int i:array){
System.out.println(i);
}
int min=array[0];
int max=0;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
if(array[i] < min){
min=array[i];
}
if(array[i] > max){
max=array[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Largest element of the Array is:"+max);
System.out.println("Smallest element of the Array is:"+min);;
}
}7import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pairs {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the numer of elements");
int num=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the Array of elements");
int array[]=new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){
array[i]=scanner.nextInt();
}
int maxDiff=0,minDiff=0;
int n1=0,n2=0,n3=0,n4=0;
for (int i=0; i < num; i++){
for (int j=i+1; j < num; j++){
if(maxDiff<array[i]-array[j]){
maxDiff=array[i]-array[j];
n1=i;
n2=j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("The Maximum Difference Pair is: %d and %d",array[n1],array[n2]);
for(int i= 0;i<num;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<num;j++){
if(minDiff>array[i]-array[j]){
minDiff=array[i]-array[j];
n3=i;
n4=j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("\n The Minimum Difference Pair is : %d and %d",array[n3],array[n4]);
}
}8import java.util.Scanner;
public class SubArray {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the numer of elements(greater than 8)");
int num=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the Array of elements");
int array[]=new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){
array[i]=scanner.nextInt();
}
int start=3;
int end=8;
System.out.println("The subArray of array elements betwen 3 and 8");
for (int i = array[start]; i <array[end]; i++){
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
System.out.print("The Array Elements are: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}2,4import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int array[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 array of elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array Elements:");
for (int i:array){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Enter the element to find:");
int element=scanner.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
if (array[i]==element){
System.out.println("The element find at index " + i);
break;
}
}
int secondArray[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Reverse Order:");
for (int i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--){
secondArray[i]=array[i];
System.out.print(secondArray[i]+" ");
}
}
}3.import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int number,positive=0,negative=0,evenNo=0,oddNo=0,zeroNo=0;
System.out.println("Enter the array elements :: ");
for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
number=sc.nextInt();
if (number>0){
positive++;
}
if (number<0) {
negative++;
}
if (number%2==0) {
evenNo++;
}
if (number%2!=0){
oddNo++;
}
if (number==0) {
zeroNo++;
}
}
System.out.println("no of positive numbers"+positive);
System.out.println("no of negative numbers"+negative);
System.out.println("no of odd numbers"+oddNo);
System.out.println("no of even numbers"+evenNo);
System.out.println("no of zeroes"+zeroNo);
}
}5.import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum = sum + arr[i];
product = product * arr[i];
}
System.out.println("sum of array : " + sum);
System.out.println("product of array : " + product);
}
}6.import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num;
System.out.println("Enter array size ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[num];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int max = 0;
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("max element is " + max );
System.out.println("min element is " + min);
}
}8.import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the array size : ");
int num=sc.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[num];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of an array :");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements in an array :");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Enter the start index and the end index : ");
System.out.println();
int start_index=sc.nextInt();
int end_index=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Sub Arrays :");
for(int i=start_index;i<=end_index;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1,2import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques12{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Elements of array");
for (int i : a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.print("Enter the number to find in array:");
int check = sc.nextInt();
int flag=0,i;
for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] == check) {
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1){System.out.println("Element found at index :"+i);}
else {System.out.println("Element Not Found...");}
sc.close();
}
}3import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a[]=new int[20];
int i,numodd=0,numeven=0,posi=0,neg=0;
System.out.println("Enter the elements :");
for(i=0;i<20;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
if(a[i]>0){posi++;}
else neg++;
if(a[i]%2==0){ numeven++;}
else numodd++;
}
System.out.printf("Number of positive: %d%nNumber of negative: %d%nNumber of Odd: %d%nNumber of Even: %d",posi,neg,numodd,numeven);
sc.close();
}
}4import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int i=0;
int a[]=new int[10];
int b[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements : ");
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
i=0;
for(int j=a.length-1;j>=0;j--,i++){
b[j]=a[i];
}
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(b[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}5import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int[10];
int sum=0,prd=1;
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
sum+=a[i];
prd*=a[i];
}
System.out.printf("Sum = %d %nProduct = %d",sum,prd);
sc.close();
}
}6import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int[10];
int grt=0,les=0;
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
if(i==0) grt=les=a[i];
else if(a[i]>grt){
grt=a[i];
}
else if(a[i]<les){
les=a[i];
}
}
System.out.printf("Largest = %d %nSmallest = %d",grt,les);
sc.close();
}
}7import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int[10];
int b[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
b[i]=a[i];
}
Arrays.sort(b);;
int e1=0,e2=0,e3=0,e4=0;
int len=b.length -1;
for (int i=0; i<=len; i++) {
if(b[0]==a[i]){ e3=e1=i;}
if(b[1]==a[i]){ e2=i;}
if(b[len]==a[i]){e4=i;}
}
int mindiff=b[1]-b[0];
int maxdiff=b[len]-b[0];
System.out.printf("maximum difference = %d of element %d and %d%nMinimun difference = %d of elements %d and %d",maxdiff,e3,e4,mindiff,e1,e2);
sc.close();
}
}8import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter array elements :");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int startInd=3,endInd=8;
System.out.printf("SubArray List... Starts at %d End at %d %n",startInd,endInd);
for(int i=startInd; i<=endInd; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.*;
public class Single1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10]; // array declaration
System.out.println("Enter 10 elements : ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
System.out.print("The Elements in array are: \n");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}2import java.util.Scanner;
public class Single2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements : ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the number to be searched : ");
int num=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(arr[i]==num){
System.out.println("Number found...");
}
}
}
}3import java.util.*;
public class Single3{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int positive=0,negative=0,oddNumber=0,evenNumber=0,sum=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[20];
System.out.println("Enter 20 elements: ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
if(arr[i]>0){
positive++;
}
else if(arr[i]<0){
negative++;
}
else{
sum++;
}
if(arr[i]%2==0){
evenNumber++;
}
else{
oddNumber++;
}
}
System.out.print("Number of positive numbers: "+positive+"\nNumber of negative numbers: "+negative+"\nNumber of odd numbers: "+oddNumber+"\nNumber of even numbers: "+evenNumber+"\nSum of zero's: "+sum);
}
}4import java.util.*;
public class Single4 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter 10 elements : ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Reveresed array :");
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int num[]=new int[arr.length];
num[i]=arr[i];
System.out.print(num[i]+" ");
}
}
}5import java.util.*;
public class Single5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int sum=0,product=1;
System.out.println("Enter the size of an array : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the elements :");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sum=sum+arr[i];
product=product*arr[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of array : "+sum);
System.out.println("Product of array : "+product);
}
}6import java.util.*;
public class Single6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the elements : ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int min=arr[0];
int max=arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(arr[i]<min)
min=arr[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(arr[i]>max)
max=arr[i];
}
System.out.printf("Largest number is : %d \nSmallest number is : %d",max,min);
}
}7import java.util.Scanner;
public class Single7 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the numer of elements : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the elements : ");
int arr[]=new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int max=0,min=0;
int n1=0,n2=0,n3=0,n4=0;
for (int i=0; i < n; i++){
for (int j=i+1; j < n; j++){
if(max<arr[i]-arr[j]){
max=arr[i]-arr[j];
n1=i;
n2=j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("The Maximum Difference is: %d and %d",arr[n1],arr[n2]);
for(int i= 0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(min>arr[i]-arr[j]){
min=arr[i]-arr[j];
n3=i;
n4=j;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("\n The Minimum Difference is : %d and %d",arr[n3],arr[n4]);
}
}8import java.util.*;
public class Single8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]= new int[10];
System.out.println("Enter the 10 elements : ");
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int num[]= new int[4];
int j=0;
for(int i=4; i<8;i++){
num[j]=arr[i];
j++;
}
System.out.println("Sub arrays :");
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
System.out.println(num[i]);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
package Discussion89;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ques3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int arr[] = new int[6];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter elements :");
//System.out.println(arr.length);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int positive = 0;
int negative = 0;
int zero = 0;
int odd = 0;
int even = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
positive++;
}
if (arr[i] < 0) {
negative++;
}
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0) {
even++;
} else {
odd++;
}
if (arr[i] == 0) {
zero++;
}
}
System.out.println("positive num: " + positive);
System.out.println("negative num: " + negative);
System.out.println("odd num: " + odd);
System.out.println("even num: " + even);
System.out.println("zero num: " + zero);
sc.close();
}
}
public class Ques5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int arr[] = new int[6];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Size of array : ");
int size=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter elements :");
//System.out.println(arr.length);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0,prod=1;
for(int ele:arr) {
sum=sum+ele;
prod=prod*ele;
}
System.out.println("Sum :" + sum +"\nProduct: "+ prod);
}
}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1package Array Single89; import java.util.Scanner; public class InputNumber{ } 2import java.util.Scanner; 3import java.util.Scanner; public class IntegerInput { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
4import java.util.Scanner; public class ReverseArray { } 5import java.util.Scanner; } 6import java.util.Scanner; |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code7import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxMinDiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr = new int [4];
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter elements");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i]=Integer.parseInt(s.nextLine());
}
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i]>max) {
max = arr[i];
}
else if(arr[i]<min) {
min = arr[i];
}}
int maxdiff = max-min;
System.out.println("max difference ="+ maxdiff);
Arrays.sort(arr);
int mindiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
if(arr[i+1]-arr[i]<mindiff) {
mindiff = arr[i+1]-arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Min difference = "+ mindiff);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
7import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int[] arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int maxDiff = arr[n-1] - arr[0];
int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minIndex1 = 0;
int minIndex2 = 0;
int len = n - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
int diff = arr[i + 1] - arr[i];
if(diff < minDiff){
minDiff = diff;
minIndex1 = i;
minIndex2 = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println("max diff " + maxDiff + " -> (0, "+ len +")");
System.out.println("min diff " + minDiff + " -> (" + minIndex1 + ", " + minIndex2 + ")");
sc.close();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
8import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
while(n < 9){
System.out.println("please enter atleast 9");
n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
int[] arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(i >= 3 && i <= 8){
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Java3import java.util.Scanner; |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Java4import java.util.Scanner; } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Java5import java.util.Scanner; |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Java6import java.util.Scanner; } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code8import java.util.Scanner;
public class subArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter values");
int i,j;
int arr[] = new int[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
arr[i]=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
}
int arr1[] = new int[4];
j=0;
for(i=4;i<8;i++)
{
arr1[j]=arr[i];
j++;
}
System.out.println("Elements btw the indexes 3 and 8 is :");
for(i=0;i<arr1.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code4import java.util.*;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
int copyArr[] = new int[n];
int j=0;
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){
copyArr[j] = arr[i];
j++;
}
for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++){
System.out.print(copyArr[i]+" ");
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code5import java.util.*;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
int sum=0;
int pro=1;
for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){
sum=sum+arr[i];
pro=pro*arr[i];
}
System.out.printf(sum+" "+pro);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code6import java.util.*;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
int max=arr[0];
int min=arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]>0){
max=arr[i];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]<0){
min=arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(min);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code7import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
int max=arr[0];
int min=arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]>0){
max=arr[i];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]<0){
min=arr[i];
}
}
int maxDiff=max-min;
int minDiff=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length-1;i++){
int diff=arr[i+1]-arr[i];
if(diff<minDiff){
minDiff=diff;
int start=i;
int end=i+1;
System.out.println(start+","+end);
}
}
System.out.println(0+","+(n-1));
System.out.println(maxDiff);
System.out.println(minDiff);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code8import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int []arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
for(int i=3;i<=n-2;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
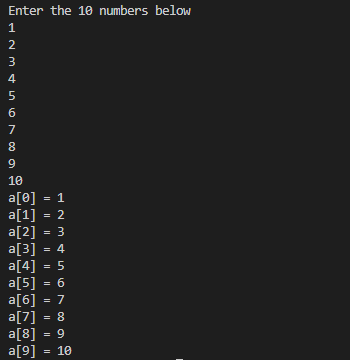
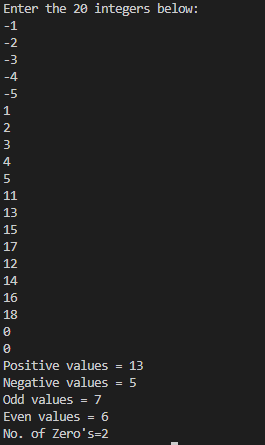
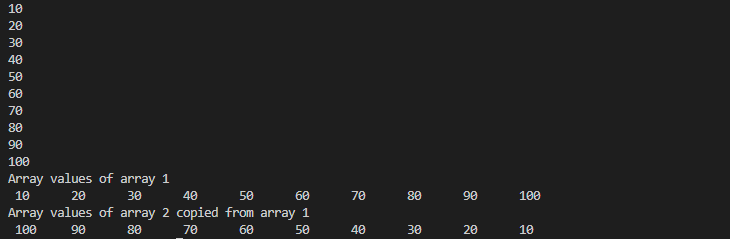
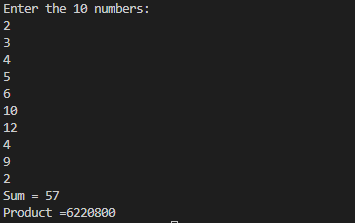
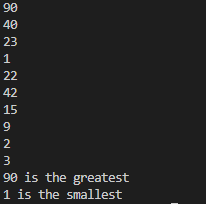
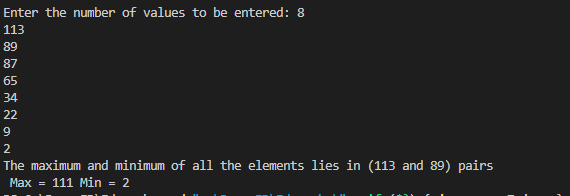
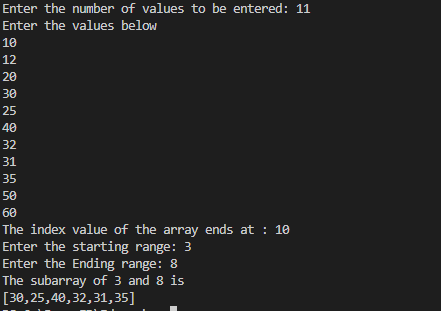
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Take 10 integer inputs from the user and store them in an array and print them on screen.
Take 10 integer inputs from the user and store them in an array. Again ask the user to give a number. Now, tell the user whether that number is present in the array.
Take 6 integer inputs from the user and print the following:
number of positive numbers
number of negative numbers
number of odd numbers
number of even numbers
number of 0s.
Take 10 integer inputs from user and store them in an array. Now, copy all the elements in an another array but in reverse order.
Consider an integer array, the number of elements is determined by the user. The elements are also taken as input from the user. Write a program to find the sum and product of all elements of the array.
Find the largest and smallest elements of an array.
Consider an integer array, the number of elements in which is determined by the user. The elements are also taken as input from the user. Write a program to find those pair of elements that has the maximum and minimum difference among all element pairs.
If the input array is [10, 12, 20, 30, 25, 40, 32, 31, 35, 50, 60], your program should be able to find that the subarray lies between the indexes 3 and 8.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions