Task - Stream API - Book Market #53
Replies: 54 comments
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
package Maps; import java.util.; class Book implements Comparable { } public class Streambook { |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
package com.java.stream;
public class Book implements Comparable<Book>{
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", author=" + author + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Book other = (Book) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.id-arg0.id;
}
}
package com.java.stream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class DriverClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Book b2 = new Book(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Book b3 = new Book(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Book b4 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
ArrayList<Book> list=new ArrayList<Book>();
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
list.add(b4);
list.stream().forEach(book ->System.out.println(book));
Set<Object> set=list.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
list.stream().sorted().forEach(book -> System.out.println(book));
list.stream().filter(book->book.quantity > 10).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
int value=list.stream().filter(b->b.id < 200).map(b ->b.quantity).reduce(0,(a ,val) -> a+val);
System.out.println(value);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Visweshwaran M Book.javaclass Book implements Comparable<Book> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Book)) return false;
Book book = (Book) o;
return id == book.id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book book) {
return Integer.valueOf(this.id).compareTo(book.id);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", Book.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("id=" + id)
.add("name='" + name + "'")
.add("author='" + author + "'")
.add("publisher='" + publisher + "'")
.add("quantity=" + quantity)
.toString();
}
}Driver Classpublic class StreamApiBook {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Book b2 = new Book(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Book b3 = new Book(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Book b4 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
books.add(b4);
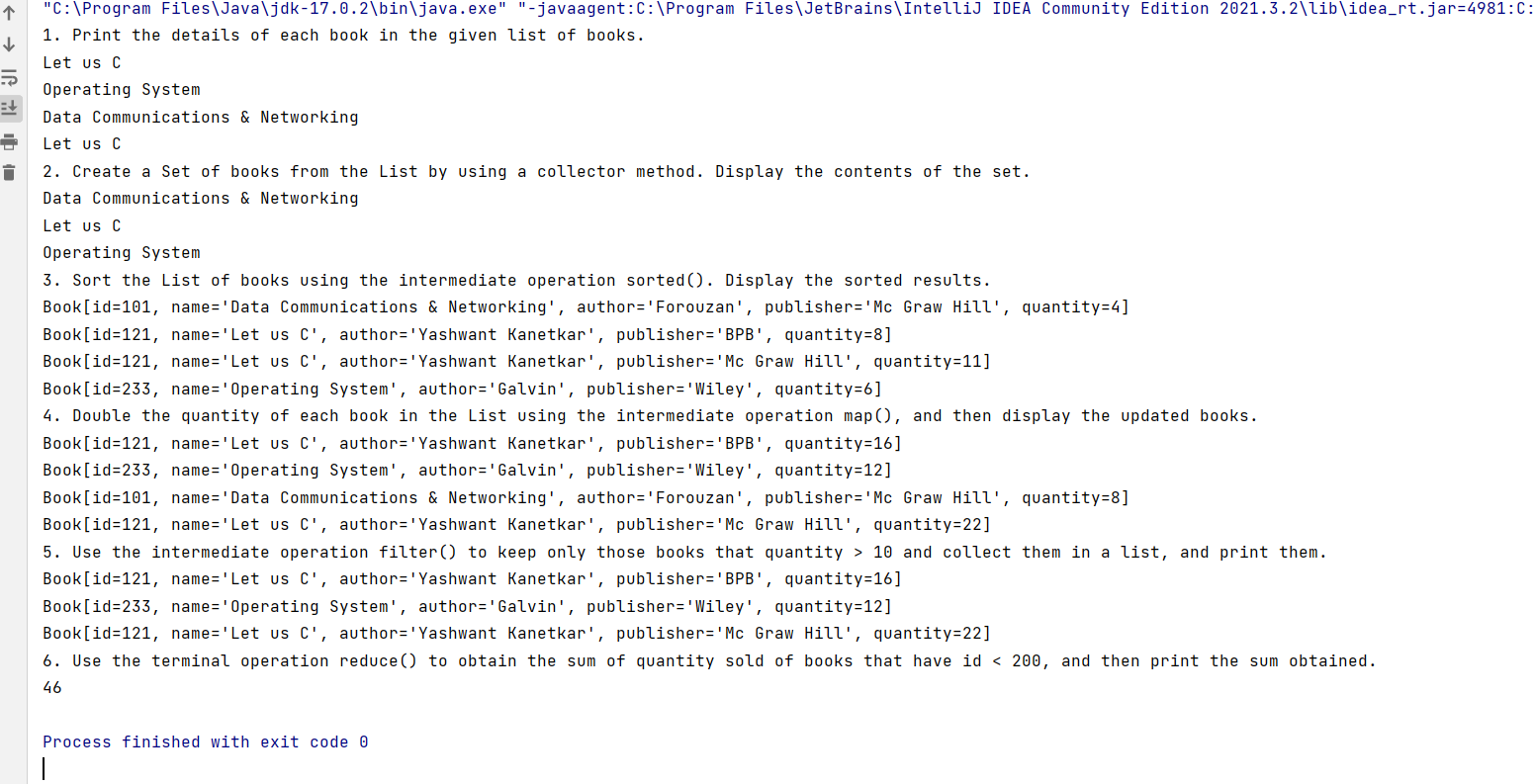
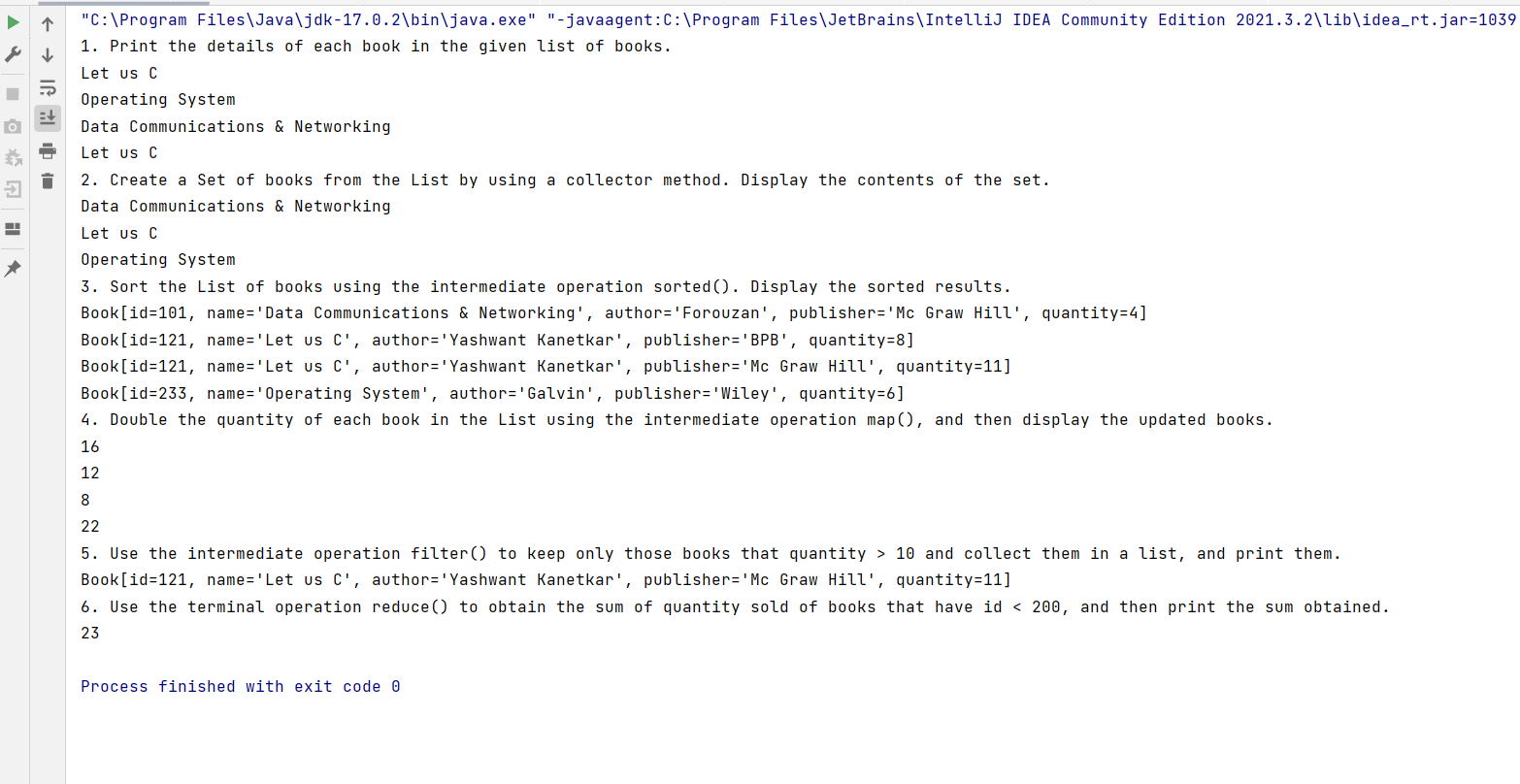
System.out.println("1. Print the details of each book in the given list of books.");
books.stream().map(b -> b.name).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("2. Create a Set of books from the List by using a collector method. Display the contents of the set.");
books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()).stream().map(b -> b.name).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("3. Sort the List of books using the intermediate operation sorted(). Display the sorted results.");
books.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("4. Double the quantity of each book in the List using the intermediate operation map(), and then display the updated books.");
//books.stream().map(b -> {
// b.quantity = b.quantity * 2;
// return b;
//}).forEach(System.out::println);
books.stream().map(b -> b.quantity * 2).forEach(System.out::println); //new
System.out.println("5. Use the intermediate operation filter() to keep only those books that quantity > 10 and collect them in a list, and print them.");
books.stream().filter(b -> b.quantity > 10).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("6. Use the terminal operation reduce() to obtain the sum of quantity sold of books that have id < 200, and then print the sum obtained.");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(b -> b.id < 200).map(b -> b.quantity).reduce(0, (sum, quantity) -> sum + quantity));
}
}Screenshots |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Bookclass Book implements Comparable<Book> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) {
return this.id-o.id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Book other = (Book) obj;
return id == other.id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", author=" + author + ", publisher=" + publisher
+ ", quantity=" + quantity + "]";
}
}# Driver Classpublic class DriverClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Book b2 = new Book(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Book b3 = new Book(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Book b4 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Book> books = Arrays.asList(b1, b2, b3, b4);
Set<Book> setofBooks=books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("Books are"+setofBooks);
books.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
List<Integer> doublequality=books.stream().map(b->(b.quantity=b.quantity*2)).toList();
System.out.println("Double the quality of each books will be"+doublequality);
List<Book> booksOfQualityGreaterthantwenty=books.stream().filter(b->b.quantity>10).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Books of Quality Greater than Twenty will be"+booksOfQualityGreaterthantwenty);
Integer sumofBooksQuality=books.stream().filter(b->b.id<200).map(b->b.quantity).reduce(0,(ans,i)-> ans+i);
System.out.println("Sum of Quality of Books"+sumofBooksQuality);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Bookpackage com.company; import java.util.Objects; public class Book implements Comparable { public Book() { public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) { @OverRide @OverRide @OverRide @OverRide Driverpackage com.company; import java.util.ArrayList; public class BookMArket { } SS |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
//Ramprasad `` package public class Book implements Comparable { } Main class package Streams; import java.util.ArrayList; public class BookStream { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
package java_programs;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
class Books implements Comparable<Books> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
// parameterised constructor
public Books(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
// override toString()
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
// override hashCode()
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
// override equals()
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Books other = (Books) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Books o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.id = o.id;
}
}
public class StreamsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Books b1 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Books b2 = new Books(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Books b3 = new Books(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Books b4 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Books> list = Arrays.asList(b1, b2, b3, b4);
//Print the details of each book in the given list of books.
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//Create a Set of books from the List by using a collector method, and then print the set.
Set<Books> set = new HashSet<>();
list.stream().forEach(set::add);
System.out.println(set);
//Sort the List of books using the intermediate operation sorted(). Display the sorted results.
list.stream().sorted(Books::compareTo).forEach(System.out::println);
//Double the quantity of each book in the List using the intermediate operation map(), and then display the updated books.
list.stream().map(e -> new Books(e.id, e.author, e.name, e.publisher, e.quantity = 2 * e.quantity))
.forEach(System.out::println);
;
// Use the intermediate operation filter() to keep only those books that
// quantity > 10 and collect them in a list, and print them.
list.stream().filter(e -> e.quantity > 10).forEach(System.out::println);
// Use the terminal operation reduce() to obtain the sum of quantity sold of
// books that have id < 200, and then print the sum obtained.
long sumData = list.stream().filter(e -> e.id < 200).map(q -> q.quantity).reduce(0,
(sum, quantity) -> sum + quantity);
System.out.println("Sum=" + sumData);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
class Books implements Comparable<Books> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Books(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Books other = (Books) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Books o) {
return this.id = o.id;
}
}
public class d53 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Books obj1 = new Books(1, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Books obj2 = new Books(2, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Books obj3 = new Books(3, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Books obj4 = new Books(4, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Books> list = Arrays.asList(obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
Set<Books> set = new HashSet<>();
list.stream().forEach(set::add);
System.out.println(set);
list.stream().sorted(Books::compareTo).forEach(System.out::println);
list.stream().map(e -> new Books(e.id, e.author, e.name, e.publisher, e.quantity = 2 * e.quantity)).forEach(System.out::println);;
list.stream().filter(e -> e.quantity > 10).forEach(System.out::println);
long sumData = list.stream().filter(e -> e.id < 200).map(q -> q.quantity).reduce(0,
(sum, quantity) -> sum + quantity);
System.out.println("Sum=" + sumData);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.ToDoubleBiFunction;
import java.util.stream.Collector;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class Book53 {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
// parameterised constructor
public Book53(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book53 [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Book53 other = (Book53) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
public class Discussion53 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book53 b1 = new Book53(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Book53 b2 = new Book53(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Book53 b3 = new Book53(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Book53 b4 = new Book53(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Book53> Library = new ArrayList<>();
Library.add(b1);
Library.add(b2);
Library.add(b3);
Library.add(b4);
System.out.println("Book List: ");
Library.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
Set<Book53> LibraryList = Library.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("Library converted to set:");
LibraryList.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
/*
* List<Book53> LibraryList2 =
* Library.stream().sorted(Book53::compareTo).toList();
* System.out.println("Sorted LibraryList: ");
*/
/* LibraryList.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println); */
List<Book53> LibraryList3 = Library.stream().map(x -> {
x.quantity *= 2;
return x;
}).toList();
System.out.println("Quantity Doubled: ");
LibraryList3.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
List<Book53> LibraryList4 = Library.stream().filter(x -> x.quantity > 10).toList();
System.out.println("Quantity greater than 10: ");
LibraryList4.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
int soldBooks = Library.stream().filter(o -> o.id < 200).map(o -> o.quantity).reduce(0, (ans, q) -> ans + q);
System.out.println("quantity sold of books having id < 200 is " + soldBooks);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class task53 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Books b1 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Books b2 = new Books(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Books b3 = new Books(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Books b4 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
ArrayList<Books> books = new ArrayList<Books>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
books.add(b4);
System.out.println("Print the details of each book in the given list of books");
books.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Create a Set of books from the List by using a collector method, and then print the set.");
System.out.println(books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sort the List of books using the intermediate operation sorted(). Display the sorted results.");
System.out.println(books.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Double the quantity of each book in the List using the intermediate operation map(), and then display the updated books.");
System.out.println(
books.stream().sorted().map(b -> new Books(b.id, b.name, b.author, b.publisher, b.quantity * 2)).toList());
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Use the intermediate operation filter() to keep only those books that quantity > 10 and collect them in a list, and print them.");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(b -> b.quantity > 10).toList());
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Use the terminal operation reduce() to obtain the sum of quantity sold of books that have id < 200, and then print the sum obtained.");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(b -> b.id < 200).map(b -> b.quantity).reduce(0, (sum, i) -> sum + i));
System.out.println();
}
}
class Books implements Comparable<Books> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Books(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Books [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Books other = (Books) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Books o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.id - o.id;
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collector;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class D53
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Books b1 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Books b2 = new Books(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Books b3 = new Books(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Books b4 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<Books> books = new ArrayList<>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
books.add(b4);
// task 1
books.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// task 2
Set<Books> bookSet = books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
bookSet.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// task 3
books.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// task 4
books.stream().sorted().map(o -> {
o.quantity = o.quantity * 2;
return o;
}).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// task 5
books.stream().filter(o -> o.quantity > 10).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// task 6
int soldBooks = books.stream().filter(o -> o.id < 200).map(o -> o.quantity).reduce(0, (ans, q) -> ans + q);
System.out.println("quantity sold of books having id < 200 is " + soldBooks);
}
}
class Books implements Comparable<Books>
{
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
// parameterised constructor
public Books(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
// override equals()
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
} else if (other == null) {
return false;
} else if (this.getClass() != other.getClass())
return false;
Books obj = (Books) other;
if (id != obj.id) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
// override hashCode()
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
return result;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Books o) {
return this.id - o.id;
}
// override toString()
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class Books implements Comparable<Books> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Books(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Books [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Books other = (Books) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Books o) {
return this.id - o.id;
}
}
public class discussion50 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Books b1 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Books b2 = new Books(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Books b3 = new Books(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Books b4 = new Books(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
ArrayList<Books> books = new ArrayList<Books>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
books.add(b4);
System.out.println("Print the details of each book in the given list of books");
books.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Create a Set of books from the List by using a collector method, and then print the set.");
System.out.println(books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Sort the List of books using the intermediate operation sorted(). Display the sorted results.");
System.out.println(books.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Double the quantity of each book in the List using the intermediate operation map(), and then display the updated books.");
System.out.println(
books.stream().sorted().map(b -> new Books(b.id, b.name, b.author, b.publisher, b.quantity * 2))
.toList());
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Use the intermediate operation filter() to keep only those books that quantity > 10 and collect them in a list, and print them.");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(b -> b.quantity > 10).toList());
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Use the terminal operation reduce() to obtain the sum of quantity sold of books that have id < 200, and then print the sum obtained.");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(b -> b.id < 200).map(b -> b.quantity).reduce(0, (sum, i) -> sum + i));
System.out.println();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collector;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class BookMarket implements Comparable<BookMarket> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public BookMarket(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
BookMarket other = (BookMarket) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookMarket [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher
+ ", quantity=" + quantity + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(BookMarket o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
class market {
public static void main(String args[]) {
BookMarket b1 = new BookMarket(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
BookMarket b2 = new BookMarket(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
BookMarket b3 = new BookMarket(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
BookMarket b4 = new BookMarket(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
List<BookMarket> book = new ArrayList<>();
book.add(b1);
book.add(b2);
book.add(b3);
book.add(b4);
System.out.println("Details of the books: ");
book.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
Set<BookMarket> s = book.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("Set of the books: ");
s.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Sorted books: ");
List<BookMarket> sortedl = book.stream().sorted().toList();
sortedl.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Doubled Quantity: ");
List<BookMarket> d = book.stream().map(x -> {
x.quantity *= 2;
return x;
}).toList();
d.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Filtered details of the books: ");
List<BookMarket> a = book.stream().filter(x -> x.quantity > 12).toList();
a.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Sum of qunatity sold: ");
int r = book.stream().filter(x -> x.id < 200).map(o -> o.quantity).reduce(0, (ans, q) -> ans + q);
System.out.println("Book sold: " + r);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
codeimport java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> {
int id;
String name;
String author;
String publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public String getPublisher() {
return publisher;
}
public int getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public void setPublisher(String publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((author == null) ? 0 : author.hashCode());
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((publisher == null) ? 0 : publisher.hashCode());
result = prime * result + quantity;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Book other = (Book) obj;
if (author == null) {
if (other.author != null)
return false;
} else if (!author.equals(other.author))
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (publisher == null) {
if (other.publisher != null)
return false;
} else if (!publisher.equals(other.publisher))
return false;
if (quantity != other.quantity)
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) {
return this.id - o.id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [author=" + author + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", publisher=" + publisher + ", quantity="
+ quantity + "]";
}
}
public class Discussion53{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "BPB", 8);
Book b2 = new Book(233, "Operating System", "Galvin", "Wiley", 6);
Book b3 = new Book(101, "Data Communications & Networking", "Forouzan", "Mc Graw Hill", 4);
Book b4 = new Book(121, "Let us C", "Yashwant Kanetkar", "Mc Graw Hill", 11);
ArrayList<Book> books = new ArrayList<>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
books.add(b4);
System.out.println("Printing using streams");
books.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("storing in set");
Set<Book> setOfBook = books.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
setOfBook.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Sorted the List of books using the intermediate operation sorted()");
books.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Double the quantity of each book in the List using the intermediate operation map()");
List<Book> booklist = books.stream().sorted().map(o->{
o.quantity = o.quantity * 2;
return o;
}).toList();
booklist.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("quantity > 10");
List<Book> Quant = books.stream().filter(x -> x.quantity > 10).toList();
Quant.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("sold of books that have id < 200");
int soldBooks = books.stream().filter(o -> o.id < 200).map(o -> o.quantity).reduce(0, (ans, q) -> ans + q);
System.out.println("quantity sold of books having id < 200 is " + soldBooks);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Book Market
Using Stream operations on a Booklist
Define a class called
Book. The skeleton of theBookclass is given below:Write the implementation for
hashCode()andequals()manually. (Important fields:id)In the driver class called
BookMarket, create four instances of theBookclass with the following:Create an
ArrayList<Book>calledbooksand insert the above book objects.Use Stream API to do the following operations:
books.Setof books from theListby using a collector method, and then print the set.booksusing the intermediate operationsorted(). Display the sorted results.map(), and then display the updated books.filter()to keep only thosebooksthatquantity > 10and collect them in a list, and print them.reduce()to obtain the sum ofquantitysold ofbooksthat haveid < 200, and then print the sum obtained.Reference
Refer to the Stream API demo program for syntax and other clues.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions